Defenitions Flashcards
(16 cards)
Chromophore
A group responsible for a compound being coloured
Stereoisomerism
Isomers that have the same structural formula, but the way the bonds are arranged in space is different
Racemic Mixture
An equimolar mixture of both optical isomers
Electrophile
An electron deficient molecule. i.e. CH3+
Polarisation
An unequal electron distribution in a covalent bond
Bond energy
The energy needed to break a covalent bond into it’s constituent atoms.
The higher the value the stronger the bond
Aromatic
A compound including a benzene ring
Homologous Series
A family of compounds that have the same general formula and contain the same functional group
Decarboxylation
The loss of a carboxyl group leading to the shortening of the Carbon chain
Hydrolysis
Decomposition by the addition of water, usually irreversibly. The added water may be in the form of water, aqueous acid or alkali
Saturated Solution
A solution in which no more solute can dissolve at that temperature
Mobile Phase (Chromotography)
A gas (in GLC) and a liquid (in HPLC) that carries the mixture through the instrumentn enabling seperation to occur on the column
Radical
A species with an unpaired electron
e.g. Cl•
Alkylation
The introduction of an alkyl group (methyl/ethyl) into the molecule.
Percentage Yield
Actual Yield x 100
Theoretical Yield
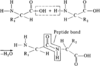
Peptide Bond