Finances Flashcards
(24 cards)
What is this formula? How is it used?

This formula finds the initial depost needed for an interest-earning account to provide enough for regular fixed withdrawals for a given number of periods. This is also called a decreasing annuity.
You can ALSO use this formula to calculate loan and mortgage payments and terms. Do this by considering a loan to be a decreasing annuity from the lender’s perspective.
What is this formula? How is it used?

This formula determines the balance at the end of a period given the balance of the previous period and a deposit. Compounding interest always calculates interest earned based on the most-recent period. This formula can be used to find the balance from period-to-period for an increasing annuity.
What is the formula for finding future value using simple interest?
\

What is this formula? How is it used?

This formula finds the future value of an account earning compounding interest to which you are making regular deposits. This is also called an increasing annuity.
What is this formula? How is it used?

This formula is used to find the interest rate per period from the annual interest rate.
What formula should you use to find the interest rate per-period given the annual interest rate?
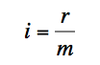
What are the variables in this equations?

n is the number of periods the account is open
F is the future value after n periods
P is the present value, the value at the beginning
i is the interest rate per period
What are the variables in this equations?

Bnew and Bprevious represent the balance in an account on two consecutive periods.
i is the interest rate per period
R is a rent payment withdrawn from the account
What are the variables in this equations?

Bnew and Bprevious represent the balance in an account on two consecutive periods.
i is the interest rate per period
R is a rent payment deposited into the account
What are the variables in this equations?

n is the number of periods this account is open
i is the interest rate per period
R is the rent, a fixed deposit being made at the end of every period
F is the future value, the final value at the end of n periods
P is not listed because it is assumed that P=0
What is this formula? How is it used?

This formula determines the balance at the end of a period given the balance of the previous period and a withdrawal. Compounding interest always calculates interest earned based on the most-recent period. This formula can be used to find the balance from period-to-period for an decreasing annuity.
What are the variables in this equations?

n is the number of periods this account is open
i is the interest rate per period
R is rent, a fixed payment *withdrawn* from the account
P is the present value, the account balance at the beginning
F is missing because it is assumed F=0
What is this formula? How is it used?

This formula finds the future value of an account with compounding interest.
What is the formula for a decreasing annuity? In what other way can this formula be used?
This formula may also be used to understand a loan or mortgage.
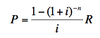
What is this formula? How is it used?

This formula finds the effective interest rate given the interest rate per period and the number of periods in a year. The effective interest rate represents the rate you would need for a simple interest-based acount to earn the same amount as a compounding interest-rate account.
What is this formula? How is it used?

This formula finds the future value of an account with simple (not compounding) interest.
What formula should you used to calculate next period’s balance using the current balance and a withdrawal?

What is the formula for finding next period’s balance using interest and a deposit?

What are the variables in this equations?

reff is the effective interest rate, which is the annual interest rate that a simple interest-earning account would need to match the earning ability of a compound-interest account.
i is the interest rate per period
m is the number of periods per year
This one actually deserves an example:
$1000 earning 12% compounded monthly goes up to $1127 (rounded to the dollar). The effective interest rate for this account is 12.7%, because it actually earned 12.7% of $1000, or $127.
What are the variables in this equation?

i is the interest rate per period
r is the annual interest rate
m is the number of periods per year
What is the formula for an increasing annuity?

What is the formula for finding future value using compound interest?
\

This formula finds the effective interest rate given the interest rate per period and the number of periods in a year. The effective interest rate represents the rate you would need for a simple interest-based acount to earn the same amount as a compounding interest-rate account.
What is this formula? How is it used?

What are the variables in this equations?

r is the annual interest rate
n is the number of years the account is open (it can be a fraction for partial years, IE six moths gives n=0.5)
F is the Future value, the value after n years
P is the Present Value, the value at the beginning


