Review 8 Flashcards
1
Q
Lactam
A
Cyclic amide
- Formed by ammonia/amine attacking COOH
2
Q
Lactone
A
Cyclic ester
- Formed by OH attacking COOH
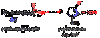
3
Q
Anhydride
A
COOH attacking COOH

4
Q
What can reduce COOH?
A
LiAlH4 (strong reducing agent)
- NaBH4 is not strong enough to reduce COOH, only aldehyde/ketone
5
Q
Beta-keto acid can be decarboxylated under _____
A
Heat (spontaneous)
- Lose C as CO2 - Anything w/ COOH and carbonyl two carbons over
6
Q
Fatty acid (w/ COOH) + strong base => _____
A
Soap (saponification)
- Long fatty tail nonpolar interior
- Carboxylate polar exterior
- Salt of carboxylate anion
7
Q
Do strong or weak bases make good LG?
A
Weak bases
8
Q
What type of molecule is ethyl acetate?
A
Ester
- Somewhat polar

9
Q
Fischer esterification
A
COOH + OH under acidic conditions

10
Q
-oate suffix
A
Ester
11
Q
React ammonia w/ anhydride => _____
A
Amide + COOH
12
Q
Inclined plane magnitude of force perpendicular to plane
A
mgcos(∂)
13
Q
Inclined plane magnitude of force parallel to plane
A
mgsin(∂)
14
Q
Normal force in inclined plane
A
mgcos(∂)
15
Q
Elastic potential energy
A
U = 1/2kx^2
16
Q
Mechanical advantage
- Efficiency
A
Fout/Fin
- E = Wout/Win
