Somatic Senses Flashcards
(20 cards)
somatic senses
1) touch
2) proprioception: awareness of body movement and location in space
3) temperature
4) nociception (pain)
- all receptors are neurons
- receptors are located in skin and viscera
- the secondary neurons in spinal cord and medulla synapse onto tertiary neurons in the thalamus
- the information is sent to the somatosensory cortex
receptor cells non-neural and neural cell
receptor cell is a non-neural cell -> primary sensory neuron -> secondary neuron -> vision, hearing, balance, taste
receptor cell is a neural cell its a primary sensory neuron as well -> secondary sensory neuron -> olfaction, somatic senses

mechanoreceptors
- pacinian corpuscles - senses vibration
- meissner’s corpuscles - responds to flutter and stroking movements
- merkel’s disks - sense stready pressure and texture
- ruffini’s endings - responds to skin stretch

adaption rate
- all sensory receptors quickly respond to the presence of stimulus. then they become used to the presence of the stimulus (they adapt to it)
- some receptors rapidly adapt to the presence of a stimulus (pacinian and meissner’s corpuscles - rapidly adapting)

receptive field size
- the area of the skin, when stimulated, influences the firing rate of a given neuron
small receptive fields - merkel (touch) and meissner (touch)
large receptive fields - ruffini (stretch) and pacinian (vibrations)
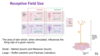
properties of skin receptors
superficial - meissner and merkel
deep - pacinian and ruffini
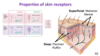
tactile acuity and the body surface
two-point discrimination - the smallest separation between two points on the skin that is perceived as two points rather than one
regions with high tactile acuity have small receptive fields

receptive fields
differences in two-point discrimination arise from the size of the receptive fields, and also from different patterns of convergence of primary sensory neurons onto secondary sensory neuron

two-point threshold

spinal cord
each segment of the spinal cord receives sensory input from a particular region of the body and supplies motor input to a similar region
from sensory receptor -> primary sensory neuron -> dorsal root ganglion -> spinal cord -> ventral root -> motor input

dermatome
a dermatome is an area of skin that is mainly supplied by afferent nerve fibers from a single dorsal root of the spinal nerve
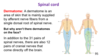
why arent there dermatomes on the face?
in addition to the 31 pairs of spinal nerves, there are also 12 pairs of cranial nerves that come directly off the brain

somatosensory pathways in the CNS
(fine touch, proprioception, vibration) - synapse with secondary sensory neurons cross the midline at the medulla
(nociception, temperature, coarse touch) - synapse with secondary sensory neurons cross the midline at the spinal cord
- goes through spinal cord, medulla, thalamus and processed at somatosensory cortex
- synapse with tertiary sensory neurons at the thalamus to the somatosensory cortex
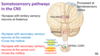
primary somatosensory cortex (S1)
- S1 made up of areas 3, 1 and 2 located on the postcentral gyrus
- primary motor cortex is located on the precentral gyrus

body map in somatosensory cortex
- the somatosensory information goes to specific areas in the cortex
- the amount of space on the somatosensory cortex devoted to each body part is proportional to the sensitivity of that part

thermoreceptors
- free nerve endings located at epidermis
- thermoreceptors in the brain - homeostasis
- cold receptors
- warm receptors
- cold and warm receptors are spread across the body
- they present slow adaption between 20-40 C but they dont adapt outside this range

pain
- pain is an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described in terms of such damage
- pain is good and important to protect you from harm
congenital insensitivity to pain
autosomal recessive disorder
pain fibers
beta fiber - large, myelinated, associated with mechanical stimuli (touch)
delta fiber - small, myelinated, associated with intense mechanical or mechanothermal stimuli, fast pain
C fiber - small, unmyelinated, associated with heat, cold, slow pain

thermoreceptors vs nociceptors
- norciceptors have a higher threshold than thermoreceptors (threshold to activate a signal from the neuron)
so when something is too hot nocicepectors (pain) receptors can increase firing rate of action potentials as temperature goes up, but thermoreceptor’s firing rate of action potentials level out at 40 degrees celsius



