The Ankle and Foot Flashcards
Each foot contains:
___ bones
___ joints
___ muscles
28 bones
30 joints
100 muscles
Primary Mobile Joint Names
- Talocrural (Talotibial)
- Subtalar (Talocalcaneal)
- Metatarso-phalangeal (MTP)
Primary Moderate Moving joints
- Midtarsal (made up of 2 joints)
- Talonavicular
- Calcaneocuboid
- Metatarsocuboid (for 4th and 5th metatarsals)
- Navicular-cuneiform (navicular with all 3 cuneiforms)
- “Lis Franc” (aka tarso-metatarsal (TMT) or cuneiform-metatarsal)
Sections of the Foot
- Hindfoot
- Calcaneus and Talus
- Midfoot
- Tarsals (navicular, cuboid and cuneiforms)
- Forefoot
- Metatarsals and Phalanges


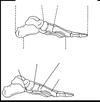

Open Kinetic Chain
Pronation
and
Supination
- Pronation
- Calcaneal
- Dorsiflexion
- Eversion
- Horizontal Abduction
- Calcaneal
- Supination
- Calcaneal
- Plantarflexion
- Inversion
- Horizontal Adduction
Open Kinetic Chain
Pronation
and
Supination
- Pronation
- Calcaneal Eversion
- Talar Plantarflexion and Horizontal Adduction
- Supination
- Calcaneal Inversion
- Talar Dorsiflexion and Horizontal Abduction
Primary Dorsiflexors muscles
–Tibialis Anterior
–Extensor hallucis longus
–Extensor digitorum longus
–Fibularis tertius
Primary Plantarflexors muscles
–Gastrocnemius
–Soleus
–Plantaris (although weak)
Secondary Plantarflexors muscles
–Tibialis posterior
–Flexor digitorum longus
–Flexor hallucis longus
–Fibularis longus
–Fibularis brevis
Primary Evertors muscles
–Fibularis longus and brevis
Primary Invertors muscle
–Tibialis Posterior
•Secondary Evertors muscle
–Fibularis tertius and Extensor digitorum longus
•Secondary Invertors
–Flexor digitorum longus, Flexor hallucis longus, TA, Ext hallucis longus
