Gravitiational Fields Flashcards
What is a gravitational force
A force of attraction that acts between objects with mass
Define Newton’s Law of Gravitation
The gravitational force between 2 masses is directly proportional to the product of the masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them
What is a uniform gravitational field
A field that exerts the same gravitational force on a mass anywhere in the field
What is a radial field
A field in which the force exerted depends on an objects position in the field. Decreases as the distance from the centre increases
Define Gravitational Field Strength
The force per unit mass exerted by a gravitational field on an object.
How does Gravitational field strength vary in a uniform and radial field
Uniform - Always the same Radial - Varies with distance
Define Gravitational potential at a point
The work done per unit mass when moving an object from infinity to that point.
Why is Gravitational potential always negative
Gravitational potential at infinity is zero, and as an object moves from infinity to a point, energy is released as the gravitational potential energy is reduced
Define Gravitational Potential Difference
The energy needed to move a unit mass between to points
What is an equipotential surface
Surfaces which are created through joining points of equal potential together, therefore the potential on an equipotential surface is constant everywhere.
What is the relationship between gravitational potential and distance between the centre of masses
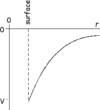
What is the gradient of a V-r graph
Gravitational field strength x -1
What is the area under a g-r graph
Gravitational potential difference
What is Keplers 3rd Law and the equation
T<strong>2</strong> is proportional to r3
T2 = r3 x 4π2/GM
Describe the context that Keplers 3rd law should be used
An object orbiting a body
M = Mass of the body being orbited
r = Dist. between the object and the centre of the body being orbitted

