Review 14 Flashcards
Which fatty acid can humans synthesize?
Palmitic acid (16:0)
When is primary oocyte made (what life stage)?
What happens to oocyte at puberty?
What happens when fertilized?
- Primary oocyte = made in fetus (b/w fertilization and birth)
- Puberty = 1˙ oocyte goes through meiosis I => 2˙ oocyte
- Fertilization = 2˙ oocyte goes through meiosis II

Hemiacetal has or does not have repeated groups?
Acetal and ketal differ how?
Does not have repeated groups
- OH, OR, R, H
Acetal has R and H w/ 2 OR’s
Ketal has 2 R’s and 2 OR’s

What type of muscle (s,c,s) is uninucleated?
Multinucleated?
Uninucleated = always smooth (sometimes cardiac)
Multinucleated = always skeletal (sometimes cardiac)
Chordate traits (mnemonic)
“Do Not Pinch People”
- Dorsal nerve cord
- Notochord
- Pharyngeal slits
- Postnatal tail
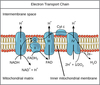
Each NADH => ____ ATP
- Total NADH => ____ ATP
Each FADH2 => _____ ATP
- Total FADH2 => ____ ATP
Total ATP/glucose = ____
Each NADH => 2.5 ATP
- Total NADH (10) => 25 ATP
Each FADH2 => 1.5 ATP
- Total FADH2 (2) => 3 ATP
Total ATP/glucose = 32 ATP
For total internal reflection to occur, light must move from high/low index of refraction to high/low index of refractions
TIR = high n to low n
- Otherwise will not occur
Rightward shift in oxy-hemoglobin curve = what type of muscle?
Exercising muscle
- Hot, hypercarbic, acidic, too much 2,3DPG
Addition of 1˙ or 2˙ amine to carbonyl
“SEe PIe”
- Secondary - enamine
- Primary - imine
If light moves from lower to higher index of refraction => it will bend (towards/away) from normal
- From higher to lower n = toward/away from normal?
Lower to higher n = bend towards normal
- Higher to lower n = bend away from normal
- The higher you get, the more you bend to become normal
Venturi effect
Fluid’s velocity becomes faster in constricted tube
- Q = Av
- Pressure decreases as velocity increases (according to Bernoulli’s)
Relate density to weight in air and weight in water
Density = (Wair) / (Wair - Wwater)
Chylomicrons
Transport mechanism for dietary triacylglycerols
- Transported via lymphatic system
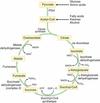
Glycolysis => ___ NADH and ____ ATP
Pyruvate DH => ____ NADH
TCA => ____ NADH, _____ FADH2, ____ GTP per glucose
Glycolysis => 2 NADH and 2 ATP
Pyruvate DH => 2 NADH per glucose
TCA => 6 NADH, 2 FADH2, 2 GTP per glucose
Causes of deviations from Hardy-Weinberg (mnemonic)
“Maggie May Does Not Smoke”
- Mutations
- Migrations
- Drift (genetic)
- Non-random mating
- Selection
Social reproduction
Perpetuation of inequalities through social institutions (ex. education, economy)
Electric field lines exit from _____ charges and enter _____ charges
Exit from positive charges
Enter negative charges
- James-Lange
- Schachter-Singer
- J-L: Arousal => Emotion
- S-S: Arousal => Interpretation => Emotion