(08) 4-49 Flashcards
(26 cards)
understand this - it’s not too bad…
sometimes it is important to measure QRS vector to make sure things are all as they should be

lead 1 - compairing electrode on right on to electrode on left
lead 2 - compare right arm to left leg (the left leg electorde is the recording one)
lead 3 - left leg to left arm
these 3 give us an idea of the QRS complex

- wilson’s central terminal is the 0 one

we can use these 6 ledas as an array around the body to record the action of the heart -
can move the electrodes so they each go through the center of the heart
then we can take our unipolar leads (green lines)
superimposed unipolar and dipolar - this gives us hexaxial lead system
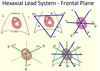
leads are marked at positive side
so lead one at 0
lead two at 60
lead three 120
positive side of aVL at -30

- Can heart rate/heart rhythm be determined from any ECG lead?
- so what is the benefit of using multiple leads?
- yes
- to get estimate of average direction of depolarization of the ventricle
- average direction is towards what?
- if it is going right and cranial - what might that imply?

- left ventricle (thickest, biggest)
- imply a thickened right ventricle

- What is the heart rate?
- as weight gets bigger?
- number of beats or complexes/min
- heart rate slower (and metabolic rate)
(Heart Rhythm)
- Describes origin of what? and somtimes what? what is the normal rhythm of the heart called?
- What is a generic term indicating slow heart rate? does it indicate origin?
- What is a generic term for fast heart rate? does it indicate origin?
(Ectoptic complex (beat, focus)
- where does it originate?
- can be what or what?
- impulses; conduction abnormalties; sinus rhythm
- bradycardia; no
- tachycardia; no
- anywhere but SA node
- premature or late (escape)
- what we we call them if they originate above the Av node?
- what do we call them if they originiate in one of the ventrciles?

- supraventricular (note that QRS still looks normal - cause ventricular pathway is normal)
- ventricular (can’t access normal Av node pathway - takes longer than normal - wider - won’t look like normal QRS complex)
understand this

(practice time)
- what is this?

- premature supraventrciular
- what is this?

- premature ventricular
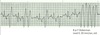
- and this?

- ventricular escape complex

- and here?

- premature ventricular (because they are different than normals)
- what is this?
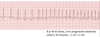

ventricular premature





- what happens in primary block?
- secondary?
- third?

- every one of the p waves is conducted - but the PQ (PR) takes a longer time
- some of the p waves are conducted - but some arents (intermittent)
- nothing goes through AV node (between atria and ventricle) - hopefully saved by ventricuar escape complexes




(Atrial Fibrillation)
- what is it?
- don’t get what waves?
- ECG characterstics?
- consequences?
- chaotic relectrical activity within atrial tissue
- p waves
- irregular rhythm (often fast)
- don’t get effective atrial contraction (don’t get topping off of blood in ventricle)
(sound like shoes in the drier)
what does this dog have?
- atrial fibrillation
what’s this
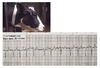
atrial fibrillation (




