1 - Hyposecretion of Anterior Pituitary Hormones Flashcards
(66 cards)
What are the two constituent parts of the pituitary gland?
Anterior Pituitary = Adenohypophysis
Posterior Pituitary = Neurohypophysis

What 6 hormones does the APG secrete?
- TSH (Thyroid Stimulating Hormone)
- LH (Lutenizing Hormone)
- FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone)
- GH (Growth Hormone)
- Prolactin
- ACTH (Adrenocorticotropic Hormone)
What is the group name for FSH and LH?
Gonadotrophins
Where does the adenohypophysial axis start?
At the hypothalamus
What role does the hypothalamus play in the adenohypophysial axis?
It makes releasing or inhibitory hormones (releasing hormones are more likely)
What defines a primary endocrine disease?
The gland at the end of the axis is functioning incorrectly.

What defines a secondary endocrine disease?
The pituitary gland itself is not functioning correctly.
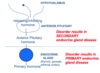
Would TSH levels be high or low in primary hypothyroidism?
TSH would be high because the pituitary is functioning, but the gland at the end of the axis is not.
Would TSH levels be high or low in secondary hypothyroidism?
TSH would be low because the pituitary is not functioning.
Name some examples of endocrine glands.
Thyroid, Adrenal Cortex, Gonads
Explain the adenohypophysial axis.
Hypothalamus
APG
Endocrine Gland
Define Hypopituitarism
Decreased production of all anterior pituitary hormones or of specific hormones
What is panhypopituitarism and how does it differ from decreased production of just some pituitary hormones?
Panhypopituitarism is decreased production of all APG hormones rather than just some specific hormones.
Which is more rare of the causes of hypopituitarism?
Congenital reasons are more rare than Acquired reasons.
Describe why Congential Panhypopituitarism occurs
- rare
- usually due to transcription factor genes mutations needed for normal APG development
- therefore, gland does not develop properly
- e.g. PROP1 mutation - deficient
What hormones are people with Congential Panhypopituitarism are deficient in?
Growth Hormone and at least one more APG hormone
What features are typical of people with Congential Panhypopituitarism?
- short stature
- hypoplastic (underdeveloped) APG on MRI
What causes are there for Acquired Panhypopituitarism?
Tumours
Radiation
Infection
Traumatic Brain Injury
Infiltrative Disease
Inflammatory (Hypophysitis)
Pituitary Apoplexy
Peri-partum infarction (Sheehan’s Syndrome)
What are the different types of tumours that can cause Acquired Panhypopituitarism?
HYPOTHALAMIC
- Craniopharyngiomas
PITUITARY
- Adenomas (benign bc not cancer but still have bad effects in body)
- Metastases
- Cysts
How can radiation cause Acquired Panhypopituitarism?
Radiation for cancer can cause hypothalamic/pituitary damage accidentally.
Growth Hormone is most vulnerable TSH is relatively resistant and it takes a long time to lose TSH after radiotherapy.
Give an example of an infection that can cause Acquired Panhypopituitarism
Meningitis
Give an example of an infiltrative disease that can cause Acquired Panhypopituitarism
Neurosarcoidosis (condition of unknown cause featuring granulomas in various tissues, involving the central nervous system).
These infiltrative diseases often involve the pituitary stalk.
What is pituitary apoplexy and how can it cause Acquired Panhypopituitarism?
Pituitary apoplexy is bleeding into or impaired blood supply of the pituitary gland. It’s typically a haemorrhage, although it is sometimes an infarction.
What is another name for Panhypopituitarism?
Simmond’s Disease