1 - Serrat - Circulation Overview Flashcards
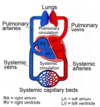
Pathway of Blood in Circulation (Start at Right Atrium)
RA -> RV -> Pulmonary Arteries -> Lungs -> Lung Capillar Beds -> Pulmonary Veins -> Left Atrium -> Left Ventricle -> Systemic Arteries -> Systemic Capillary Beds -> Systemic Veins
Heart Valves (order of flow, start at RA)
RA -> Tricuspid Valve
RV -> Pulmonary Valve
LA -> Mitral Valve
LV -> Aortic Valve
Arteries
Exception?
Carry oxygen-rich blood under high pressure from heart to body
Exception: Pulmonary Arteries carry low-oxygen blood to lungs
Veins
Exception?
Return low-oxygen blood to heart under low pressure
Exception: Pulmonary veins carry oxygen-rich blood back to the heart
What connects the arteries and veins?
Capillaries
Nutrient, O2, and waste exchange
Arterial and Vein layers
Tunica Adventitia: Outer connective tissue layer
Tunica Media: Middle smooth muscle layer, most variable layer in thickness and elastic fibers, controls arterial vasomotor tone
Tunica Intima: Inner lining of endothelial cells (single layer), allows diffusion from lumen into vessel wall
What controls arterial vasomotor tone?
What does this help biologically regulate?
The smooth muscle layer and elastic fibers of the tunica media
Minimizes change in blood pressure as heart contracts and relaxes
Pulmonary Circulation
Pumps low oxygen blood from RV to lungs through pulmonary arteries
Returns oxygen-rich blood to LA via pulmonary veins
Systemic Circulation
Pumps oxygen-rich blood from LV to body through aorta
Returns blood to RA through superior and inferior vena cavae and cardiac veins
Large (Conducting) Elastic Arteries
Examples?
Layers of elastic fibers in tunica media allow expansion and recoil during cardiac cycle
Elasticity helps maintain constant flow of blood and minimized changes in blood pressure
Ex: Aorta, L-subclavian, L-common carotid, braciocephalic trunk, pulmonary trunk
Medium (Distributing) Muscular Arteries
Examples?
Composed primarily of smooth muscle in tunica media
Muscle wall allows vessel to vasoconstrict and reglate blood flow to different parts of body
Examples: Most named arteries in limbs, femoral and brachial arteries
Small Arteries and Arterioles
What can result if degree of muscle tonus is above normal?
Narrow lumina and thick muscular walls
Arteriole smooth muscles control the filling of capillar beds and regulate the arterial pressure in the vascular system
- -
Hypertension
Atherosclerosis
Common form of arteriosclerosis (thickened walls/loss of elasticity) associated with fat and cholesterol buildup – may lead to thrombus
Thrombus
Clot formed in a blood vessel or in a chamber of the heart that remains in place of origin
Embolus and Embolism
Embolus: Blood clot that detaches from its place of origin and travels in blood strem
Embolism: Obstruction of a blood vessel due to an embolus (ex. pulmonary embolism)
How do you determine where a clot will lodge?
Smallest vessel downstream
Anastomoses
connections (communications) between branches of arteries
Prevalent around joints
Collateral Vessels
Series of smaller vessels that supply tissue in addition to its main blood supply
Prevalent around joints
What allows alternative / detours of blood flow if there are obstructions?
Anastomoses
Collateral Vessels
What are the blood sources for the hand?
Two sources
Radial / Ulnar Arteries
End Arteries
Clinical Examples?
Terminal arteries with no anastomose with adjacent arteries
Blockage interrupts tissue perfusion
- - -
Kidney has segmental blood supply w/end arteries if these are blocked–section dies (necrosis)
Venules and Small Veins
Smallest unnamed veins that drain capillaries
Venules join to form small veins
Small veins empty into larger veins and unite to form venous plexuses
Medium Veins
Drain venous plexuses and accompany medium arteries, contain small amounts of smooth muscle in walls
Have one way valves that permit blood to flow toward heart, but not in reverse
Accompanying Veins
Usually accompany deep arteries of the same name, often occur as multiple vessels in a common vascular sheath with an artery


