Renal Replacement Therapy Flashcards
AEIOU: Indications for Renal Placement Therapy
A: __ with a pH of:
E: electrolyte abnormalities with a potassium of ___ or hypo/hyper___
I: ingestions such as toxic alcoholes like ___, or medications such as ___
O: overlaod: pulmonary edema
U: ____. Associated with conditions such as __, ___ and bleeding.
R- cases that are refractory to medical therapy
A: ACIDOSIS with a pH of: <7.1
E: electrolyte abnormalities with a potassium of >6.5 or hypo/HYPERCALCERMIA
I: ingestions such as toxic alcoholes like METHANOL, ETHYLENE GLYCOL, or medications such as LITHIUM, METFORMIN, VALPROIC ACID. ONES THAT STAY IN THE VASCULAR SOACE
O: overlaod: pulmonary edema
U: UREMIA. Associated with conditions such as PERICARDITIS, ENCEPHALOPATHY and bleeding.
R- cases that are refractory to medical therapy

non urgen uremia symptomsq
anorexia, nausea, fatigue, pruritis

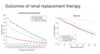
for patients with CKD, these problems often start a bit more slowly. when is the ideal time to start renal reaplcement?
you can start a bit later; eariler dialysis initiation was not associated with improved outcomes. Often, they slowly develop the non-urgen symptoms. in AKI, earlier dialysis was also not associated with improved outcomes.

4 renal replacement therapy modalities
- transplant
- hemodialysis
- peritoneal dialysis
- conservative care
Dialysis is the diffusion of molecules in solution across a __ __ along an _ __ gradient
The goal is to restore the __ and __ compartments, as seen in normal kidney function in a fail safe manner
Dialysis is the diffusion of molecules in solution across a semipermeable membrane along an electrochemical concentration gradient
The goal is to restore the intracellular and extracellular compartments, as seen in normal kidney function in a fail safe manner

pros of AV FISTULA hemodialysis
reliable access
good long term patency
lower risk of infection and thrombosis
cons of AV FISTULA hemodialysis
- requires a surgical procedure
- takes 3 months to mature
- only 40% mature
- steal syndrome is a possibililte
- heart failure
- aneurysms with risk of rupture
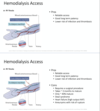
pros of AV GRAFT hemodialysis
less time to mature
can be used in patients running out of vascular access options

cons of AV GRAFT hemodialysis
infection
thrombosis
venous hypertension
pseudoaneurysms
steal syndrome
most favorable hemodialysis method for CKD
AV fistula hemodialysis since it lasts a long time
Central Venous Catheter hemodialysis pros
can be used right away
can be inserted at bed side
cons of central line hemodialysis access
infection
catheter dysfunction
thrombosis
central vein stenosis
define steal syndrome
So much blood flowing through the fistula that less blood is flowing to the distal digits. May have ulceration, coldness in fingers etc.
seen in fistula and AV graft hemodialysis methods
outline the first second and third line places of types of hemodialysis
we basically use AV Graft when there’s not many options

when someone is on hemodialysis they must receive ___ medications. outline some of the meds used
ANTIGOAULATION THERAPY. helps prevent clotting of blood in the dialysis filter.
- heparin
- lower molevular weight heparin
- HITT
- citrate
- saline flush