Lecture 1: Logic Flashcards
(30 cards)
What is a deductive argument?

What is a premise?
A sequence of statements from our previous body of knowledge
What is a conclusion?
a new statement typically not included in our previous body of knowledge
A deductive argument is valid iff
A deductive argument is valid if and only if it makes it impossible for the premises (the “old knowledge”) to be true and the conclusion (the “new knowledge”) to be false
Does a valid deductive argument require the premise to be true?
NO
The validity of an argument does not rely on the truth/falseness of is statements, but..
In the relationship between these statements
Why does logic need to be formalized?
- to make the sbtract skeleton of arguments more evident
- Because reasoning expressed in informal natural language can be flawed (natural language is ambiguous and tricky).
What are the three levels of formalization?

Each complex sentence in any natural language is made up of
Atomic propositions (atoms)
What are atoms
The smallest syntactical units of a speech that convey an independent piece of information that can be assigned a truth value of True or False
Atoms are joined together by
Conjunctions
A proposition is a declarative sentence that is…
unanbiguously true or false
All propositions are constructed assembling…
Atomic propositions (atoms) via connectives
The truth table of a proposition is uniquely and algorithmically dtermined by its
Connectives and by the truth values of its atomic consituents
What are WFFs

What is the precedence of connectives?

In logic, the semantics of a proposition is limited to…
Its truth value
Each atom can have… with the exception of…

With sentences using the english word “or” you must be careful…
Of whether or not it is an OR or an XOR
What is the truth table of the conditional (implication)
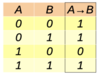
A conditional statement does not imply…

What are some english versions of the conditional statement?

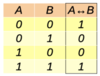
What is the truth table of the biconditional?