11: DNA & RNA structure and function Flashcards
(29 cards)
Mendel’s 3 findings on genetics
- genes are on chromosomes
- gene mutations cause metabolic errors
- DNA is made up of nucleotides
What are the 4 nucleotides that make DNA?
- Adenine
- Cytosine
- Guanine
- Thymine
How is a nucleotide of DNA structured?
- 1 base
- 1 phosphate group
- 1 sugar deoxyribose
Chargaff’s Rules
nucleotide bases are found in specific proportions
- amount of A, C, G, T differs btwn species
- amount of A = T amount of C = G
Rosalind Franklin findings. What did she use?
- used x-ray crystallography
- DNA is helical
Watson & Crick findings
- The sugar and phosphate groups are bonded (ladder)
- Bases are joined by hydrogen bonds (rungs of ladder)
- complementary bases (A&T, C&G)
DNA Replication
- original strands serve as templates
- 1 original strand is present in new helix
Origins of Replication
where DNA replication is initiated along the DNA strand
Replication Bubbles
splitting of DNA helix in origin of replication site
RNA structure
- Adenosine
- Cytosine
- Guanine
- Uracil (sugar ribose)

m(RNA)
what does it carry? where is it made?
- messenger RNA
- produced in nucleus through transcription
- carries genetic info from DNA to cytosol
t(RNA)
what does it do? how many types?
- transfer RNA
- carries amino acids to protein synth. site
- 20 different types for 20 different amino acids
- amino acid on one end and an anticodon on the other end

r(RNA)
what do they do?
- ribosomal RNA
- 2 r(RNA) join with proteins in cytosol to form subunits of ribosomes
How does DNA make protein?
genes in DNA contain instructions for amino acid sequence of a protein
What happens if there is an error in a gene for an enzyme?
- becomes non-functional
- biochemical pathway may be affected
- can create inborn errorsin metabolism that lead to metabolic diseases
What does the sequence of amino acid determine for a protein?
unique shape and function
Transcription
synth of m(RNA) from template DNA
Translation
m(RNA) directs the sequence of amino acids in the protein
Triplet Code
info for amino acid sequence of a protein encoded within a gene
Codons
where are they found? what do they provide?
- in m(RNA)
- how triplet code is transcribed
- provide redundant sequences for the placement of amino acids in a protein
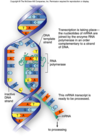
DNA Transcription
- RNA polymerase binds to DNA promoter of a gene
- DNA helix unwound
- primary mRNA strand is formed
- mRNA is complementary to DNA sequence
Anticodons during Translation
- mature RNA moves to a ribosome
- sequence of codons dictates sequence of complimentary anticodons
- order of t(RNA) molecules determines order of amino acids
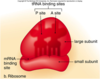
3 phases of Translation
- Initiation: small ribosomal subunit, large ribosomal subunit, the mRNA, and a tRNA carrying a methionine bond to the mRNA to start transcription
- Elongation: amino acid sequence is extended
- Termination: when protein synth is done

What does Gene Mutation do to the DNA?
changes the seqence of bases


