Introduction to Dermatology Flashcards
What is the largest organ in the body?
Skin
What are some skin adnexal structures?
Hair
Nails
Glands
Sensory structures
What are important functions of the skin?
- Protection
- Homeostasis
- Transmission of sensation
What are the layers of the skin from superficial to deep?
Epidermis
Dermis
(then below but not part of the skin is the hypodermis)

What are the layers of the skin from superficial to deep (invidividual layers)?
Stratum corneum
Stratum lucidum
Stratum granulosum
Stratum spinosum
Stratum basale

What forms the stratum corneum?
Dead cells with a hard protein envelope
Cells contain keratin and are surrounded by lipids

What forms the stratum lucidum?
Dead cells lie within despersed keratohyalin

What forms the stratum granulosum?
Keratohyalin and a hard protein envolope
Lamellar bodies release lipids
Cells die

What forms the stratum spinosum?
Keratin fibres and lamellar bodies accumulate

What forms the stratum basale?
Cells divide by mitosis and some of the newly formed cells become the cells of the more superficial streta
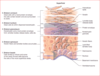
What within the skin releases lipids?
Lamellar bodies
What is A?
Hyponychium
What is B?
Nail plate
What is C?
Lateral nailfold
What is D?
Nail bed
What is E?
Lunula
What is F?
Cuficle
What is G?
Proximal nailfold
What is H?
Nail matrix
What are the 3 different stages of the hair cycle?
Anagen
Catagen
Telogen
What is the anagen phase of hair cycle?
Active growing phase
What is the catagen phase of hair cycle?
2-3 week phase growth stops/follicles shrink
What is the telogen phase of hair cycle?
Resting phase for 1-4 months
How long does the telogen phase of hair cycle last?
1-4 months
How long does the catagen phase of hair growth last?
2-3 weeks
During what phase of the hair cycle is most hair in?
Anagen (80-90% hair)
Telogen (up to 10% of hair)
Categen (1-3% of hair)


