P3: Circuits Flashcards
What are the units for current?
Amps (A)
Identify the circuit symbol

Cell
Which circuit component pushes charge (electrons) around a circuit?
A cell or battery
Identify the circuit symbol

Bulb
Identify the circuit symbol

Voltmeter
What is meant by electrical current?
The amount of charge flowing per second
Which component can we use to control whether or not current can flow in a circuit
A switch
Identify the circuit symbol

Motor
The charged particles that move around a circuit are called…
electrons
Which component do we use to measure electric current?
Ammeter
Identify the circuit symbol

Switch
Identify the circuit symbol

ammeter
Two or more cells make up a…
……..battery
Identify the circuit symbol

Battery
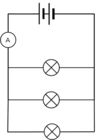
Identify the type of circuit shown.

Series Circuit