Thyroid Gland Flashcards
Describe the anatomy of the thyroid

Bi lobed, slightly asymmetrical, by the trachea

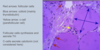
Use this image to explain the histology of the thyroid gland

lined by follicular cells
The colloid is where TH is stored, after being synthesised by the activity of follicular cells.
What are the thyroid hormones?
Thyroid hormones are derived from two iodinated tyrosine molecules:
T4: major form released to blood, less active (prohormone- needs to be activated before it becomes effective)
T3: active form, converted in target cells
Describe the synthesis of thyroid hormones
Active I- uptake across basolateral membrane by Na/I symporter (NIS). Stimulated by TSH.
Iodide efflux across apical membrane via pemdrin exchanger.
At extracellular apical membrane iodide is oxidized–>iodine and bound to tyrosine residues w/in thyroglobulin (TG). This requires thyroid peroxidase (TPO) and H2O2.
Tyrosine residues are iodinated in 1(MIT) or 2(DIT) positions.
Coupling of iodotyrosine residues produces T4 (DIT-DIT) and slightly less T3 (MIT-DIT).
Describe Thyroid hormone action on target tissues
TH receptors (TRs) belong to the nuclear receptor superfamily- these are all ligand-activated transcription factors
High affinity for T3 than T4
Activation requires dimerization with another TR or retinoid X receptor (RXR)
TRs encoded by two genes: TR alpha and TR beta
Describe the metabolic regulation of THs
Deiodinases: family of 3 enzymes that activate or inactivate TH, important for TH homeostasis.
Tissue-specific expression of these enzymes can control the generation of T3 at the level of the target tissues.
At the cellular level, D3 decreases TH action and D2 increases it.
How is TSH released?
Hypothalamic neurosecretory cells release (TRH) into the portal capillaries
TRH stimulates thyrotrophs of anterior pituitary to secrete thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
This rate of secretion is controlled by negative feedback, via the hypothalamo-pituitary axis

Describe the TSH receptor and its actions
Main effects mediated via Gs and cAMP – PKA cascade.

Give the actions of TSH
Increases iodine uptake
Stimulates other reactions involved in TH synthesis (e.g., TPO)
Stimulates uptake of colloid
Induces growth of thyroid gland (which can lead to goitre- swelling of the neck) This is generally due to iodine deficiency
Describe how TSH levels can be used to diagnose hyper and hypothyroidism
Thyroid gland is overproducing thyroid hormones. These act on the anterior pit to decrease TSH levels
Hypothyroidism: thyroid gland is underproducing thyroid hormones, so TSH levels rise

Describe how TSH levels can be used to diagnose secondary hyper and hypothyroidism
Secondary hyperthyroidism: TSH levels are higher than normal eg due to acromegaly or oversecretion of TSH by the pituitary gland. The problem is not the thyroid itself.

What is graves disease?
Autoimmune- autoantibodies strongly activate TSH receptor
High circulating TH, low TSH
Weight loss, tachycardia, fatigue
Diffuse goitre (TSH receptor stimulation)
Opthalmopathy- bulging eyes

What is Hashimoto’s disease?
Hashimoto’s: primary hypothyroidism
Autoimmune
Low circulating TH, high TSH
Lethargy, intolerance to cold
Lack of growth and development
Diffuse goitre due to high circulatory TSH levels

