CH 1-6 Flashcards
The Definition of Biology
Biology is the study of life
Atom
Smallest unit of matter
Molecule
More then one atom bound together
Organelle
“little organ” a specialized cellular part
Cell
Smallest unit of life
Tissue
Multiple cells working together to preform a function
Organ
Multiple tissues working together to perform a function
Organism
A single living being
Population
Multiple organisms of the same species living in a given area
Communities
Several populations of different species living in the same area
Ecosystem
All organisms and non-living matter in a given area
Biosphere
All Ecosystems combined
The Scientific Method

_______ is anything that occupies space and has mass
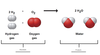
Matter is anything that occupies space and has mass
Matter is composed of ___________
Matter is composed of Chemical Elements
Elements are substances that ______ be broken down into outher _____
Elements are substances that cannot be broken down into outher substances
There are ___ naturally occurring elements on Earth
There are 92 naturally occurring elements on Earth
___ elements are essential for life
25 elements are essential for life