BB Anatomy 1 COPY Flashcards
the central sulcus disects which lobes of the brain?
frontal lobe from the temporal lobe
frontal lobe from the parietal lobe
frontal lobe from the occipital lobe
frontal lobe from cerebellum
parietal lobe from temporal lobe
the central sulcus disects which lobes of the brain?
frontal lobe from the temporal lobe
frontal lobe from the parietal lobe
frontal lobe from the occipital lobe
frontal lobe from cerebellum
parietal lobe from temporal lobe
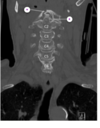
label 1-3

1: midbrain
2: the pons
3: medulla oblongata

what structure is this?
pons
medulla oblongata
midbrain
hypothalamus
fasciculus gracilis

what structure is this?
pons
medulla oblongata
midbrain
hypothalamus
fasciculus gracilis
what structure is this?
pons
medulla oblongata
brainstem
hypothalamus
fasciculus gracilis

what structure is this?
pons
medulla oblongata
midbrain
hypothalamus
fasciculus gracilis
Which of the following is A?
Pons
Medulla
Cerebral aquaduct
Fourth ventricle
Midbrain

Which of the following is A?
Pons
Medulla
Cerebral aquaduct
Fourth ventricle
Midbrain

Which of the following is B?
Pons
Medulla
Cerebral aquaduct
Fourth ventricle
Midbrain

Which of the following is B?
Pons
Medulla
Cerebral aquaduct
Fourth ventricle
Midbrain
Which of the following is C?
Pons
Medulla
Cerebral aquaduct
Fourth ventricle
Midbrain

Which of the following is C?
Pons
Medulla
Cerebral aquaduct
Fourth ventricle
Midbrain
Which of the following is D?
Pons
Medulla
Cerebral aquaduct
Fourth ventricle
Midbrain

Which of the following is D?
Pons
Medulla
Cerebral aquaduct
Fourth ventricle
Midbrain
Which of the following is E?
Pons
Medulla
Cerebral aquaduct
Fourth ventricle
Midbrain

Which of the following is E?
Pons
Medulla
Cerebral aquaduct
Fourth ventricle
Midbrain
What are the two layers of the dura mater? [2]
- *periosteal layer** (which lines the inner surface of the bones) [1]
- *meningeal layer** which forms dural folds. [1]

Lumbar puncture needle is inserted into:
- space between arachnoid mater and pia mater
- space between dura mater and arachnoid
- space between arachnoid and pia mater
- space between vertebrae and dura mater
- into the spinal cord
Lumbar puncture with needle is inserted into:
- *- space between arachnoid mater and pia mater**
- space between dura mater and arachnoid
- space between arachnoid and pia mater
- space between vertebrae and dura mater
- into the spinal cord
Epidural needle is inserted into:
- space between arachnoid mater and pia mater
- space between dura mater and arachnoid
- space between arachnoid and pia mater
- space between vertebrae and dura mater
- into the spinal cord
Epidural needle is inserted into:
- space between arachnoid mater and pia mater
- space between dura mater and arachnoid
- space between arachnoid and pia mater
- space between vertebrae and dura mater
- into the spinal cord
which side of spinal cord carries motor fibres? [1]
which side of spinal cord carries efferent fibres? [1]
which side of spinal cord carries motor fibres? [1]
ventral root
which side of spinal cord carries efferent fibres? [1]
dorsal root
which out of A & B is the dorsal root and ventral root?

A: dorsal root - look out for DRG. DORSAL IS BIGGER
B: ventral
describe the overview of 1st order, 2nd order & 3rd order neuron pathways [3]
first order neurons: peripheral receptors –> spinal cord, where is will synapse with second order neurons in the spinal cord or brainstem.
second order neurons:spinal cord –> brain, usually the thalamus.
third order neurons: thalamus –> primary sensory cortex.

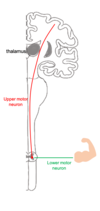
describe basic pathway of descending tracts: first order and second order neurons
first order neuron: (aka upper motor neuron): brain to the spinal cord or brainstem.It will synapse with the second order neuron,
second order neuron (aka lower motor neuron): spinal cord –> skelatal muscle