17. Embryonic Development 🧠 Flashcards
(28 cards)
What is the name given to the proliferation of the ectoderm in the dorsal midline?
Neural plate
What happens to the neural plate as it thickens?
- It folds up the sides and eventually the two neural folds fuse to form a tube
- The space in the middle is the neural canal/neural groove

What is the name given to the bunch of cells at the tip of the neural fold that are excluded in the fusion?
Neural crest

Which cells do the neural tube and neural crest cells give rise to?
- Neural tube – all cells of the CNS
- Neural crest – all cells of the PNS

What is the name given to the wall of the neural tube?
Neuroepithelium

What three types of cells do neuroepithelium give rise to?
NEG
-
Neuroblasts
- Postmitotic cell that does not divide further and will develop into a neuron after migration
- Neuroblasts differentiate from radial glial cells (progenitor cells responsible for forming neurons in the cerebral cortex)
- Ependymal cells
- Neuroepithelial lining of the ventricular system of the brain and central canal of the spinal cord
- Ventricular system = lateral ventricles (R+L), 3rd and 4th ventricle
- Neuroepithelial lining of the ventricular system of the brain and central canal of the spinal cord
-
Glioblasts
- these become neuroglia (astrocytes + oligodendrocytes)

Are motor neurons produced from neuroepithelium?
- Yes – although most of their axons are outside the CNS, their cell bodies are within the spinal cord
- More neural tube than neural crest)

State four cell types that neural crest cells can differentiate into.
N SAS
- Non-neuronal cells e.g. melanocytes
- Sensory neurons of dorsal root ganglia and cranial ganglia
- Autonomic post-ganglionic neurons
- Schwann cells
Describe the arrangement of the neuroepithelium.
- Neuroepithelium has an inner layer and an outer layer
- Most cells are connected to both the inner and outer layer but the nuclei are at different positions

Describe the differentiation of the neuroepithelium
- Cell withdrawal away from the outer membrane towards the inner membrane
- Mitosis at the inner membrane
- One of the daughter cells will remain attached to the inner membrane and the other daughter cell will move away from the inner membrane and become a neuroblast
- The neuroblast will develop processes and one will become the axon
- These axons are directed away from the inner membrane
- Three layers are formed
- Grey matter
- White matter
- Ependymal cell
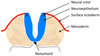
What are the three layers formed by the differentiation of the neuroepithelium?
- Ependymal
- Grey matter
- White matter AKA germinal layer, mantle layer, marginal layer

Glioblasts show a similar pattern of differentiation to neuroblasts. State one difference.
- Glioblasts can migrate into the white matter
- NOTE: glioblasts do not develop axons (but they do develop processes)
What guides the process of differentiation and migration?
Signalling molecules
Which factors are important with regards to signalling molecules?
Concentration and timing
What can the grey matter of the neural tube be divided into?
Alar plates and basal plates

Which types of neurons do the alar plate and basal plate give rise to?
- Alar plate – interneurons
- Basal plate – interneurons and motor neurons

Which structures around the neural tube release signalling molecules and what effect do they have on the cells in the neural tube?
-
Ectoderm
- produces signalling molecules that inhibit the cells nearest to it from differentiating into motor neurons
-
Notochord
- releases signalling molecules that induce the cells nearest to it to differentiate into motor neurons

Around 4 weeks, you get differentiation of the wall of the anterior neural tube to form three primary vesicles. Name these primary vesicles.
PMR
-
Prosencephalon
- Future forebrain
-
Mesencephalon
- Future midbrain
-
Rhombencephalon
- Future hindbrain

Describe the changes that occur to these three vesicles in the week or so following their formation.
- The first and third vesicles divide in two
-
Prosencephalon
-
Diencephalon
- Thalamus
- Hypothlamus
- Subthalamus
- Epithalamus
-
Telencephalon
- Cerebrum
- Cortex & subcortical structures (hippocampus, basal ganglai, olfactory bulb)
- Cerebrum
-
Diencephalon
-
Rhombencephalon
-
Metencephalon
- Pons
- Cerebellum
-
Myelencephalon
- Medulla oblongata
-
Metencephalon

What important structure begins to appear quite late in development (around 8 weeks) and where does it appear from?
- Cerebellum – appears as an out pouching from the back of the pons
- From the metencephalon (originally the rhomboncephalon)
Name the three flexures in the developing brain.
- Cephalic
- Pontine
- Cervical

Describe the formation of the 4th ventricle.
- In the neural tube in the region that will become the brainstem, the roof plate rapidly proliferates and causes the alar plates to split apart so that they are lateral to the roof plate
- The space left from the proliferation of the roof plate will become the 4th ventricle
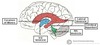
Describe the arrangement of motor, sensory and autonomic cranial nuclei within the brainstem.
- Motor = medial
- Sensory = lateral
- Autonomic = in between

What structure divides the motor nuclei from the sensory nuclei in the brainstem?
Sulcus limitans





