17 - Marine Weather Flashcards
(23 cards)
Heating of the Earth
- Curved Earth = Sun rays hit Earth at all angles
- Uneven heating of the Earth causes differences in air density in a change in pressure
Winds and Currents
Air flows from areas of high pressure into areas of low pressure
Types of motion in the atmosphere
- Vertical (currents)
- Horizontal (wind)
- Factors that contribute to winds and currents
- Air pressure
- Temperature changes
- Coriolis force
Air masses & fronts
A large body of air with generally uniform temperature & humidity
Front
Boundary layer between two types of air masses
- Different characteristics
- Types of Fronts
- Warm
- Cold
- Stationary
- Occluded
Warm Front

- Slides over and pushes the cold air
- Brings lighter but longer lasting rain

Cold Front

- Moves faster
- Pushes the warm air up
- Shorter rainfall
- Brings heavy storms/rains

Stationary Front

- When a cold front meets a warm front and none has the strength to push the other
- No movement between the fronts
- Rain may fall for many days

Occluded Front

- When a cold front catches a warm front, and the warm air lifts off the ground
- Can be cold or warm occluded depending on the temp. of the cold front
- Has both cold and warm front characteristics
- Heavy rain on cold side
- Light rain on warm side

Fog
Forms when warm, moist air blows over a colder surface and is cooled below its dew point
- Advection Fog is the most common type of fog

What are the two kinds of pressure systems?
- High Pressure
- Low Pressure
Circulation is on the opposite direction of the Southern Hemisphere
- i.e. High Pressure goes CCW, Low Pressure goes CW
High Pressure System
- Surface winds blow clockwise around a high pressure & diverge
- Generally areas of dry descending air
- Good weather is associated

Low Pressure System
- Surface winds blow counterclockwise around a low pressure & converge
- Sudden decrease in pressure
- Sudden decrease in temperature
- Sudden change in wind direction
- Bad weather is associated

Hurricanes
Form when a low air pressure system develops over warm ocean waters with special wind patterns to propel them

Eye of the Hurricane characteristics
- Extremely low pressure
- Calm weather
- Surrounded by thunderstorm wall
Right side of the Hurricane
Dangerous Semicircle
- Wind on the STBD Bow
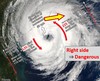
Left side of the hurricane
Navigable Semicircle
- Wind on the STBD Quarter

Ship instruments for Pressure
- Aneroid Barometer (commonly used)
- Used in millibars/in. of mercury
- Permanently mounted
- Calibrated by Port Meteorloical Officer
- Barograph
- Monitors pressures over time (similar to a seismograph)
Ship instruments for Temperature
- Thermometer
- Air Temp
- Hull of the Ship
- Sea Water Temp
- Can be used to create fog models
Ship instruments for Humidity & Wind
- Humidity
- Hygrometer
- Wind
- Wind Speed uses anemometer
- Wind Direction uses a Wind Vane
- Combination of the two is called a Aerovane
Meteorology & Oceanography
- Known as METOC
- Naval Maritime Forecast Center, Pearl Harbor, HI
- Naval Maritime Forecast Activity, Norfolk, VA
- Dedicated Maritime Security
- 24/7 Global coverage
Optimum Track Ship Routing (OTSR)
- Advises ships on where to travel based off prevailing weather
- Requested via MOVREP
- Advisories and recommendations are based on individual ship’s operating limits
- Can be modified based on operational constraints or operational commander’s approval
METOC Products
–Optimum Track Ship Routing (OTSR)
–Ship weather forecasts (WEAX)
–Aviation weather forecasts for ship-based helicopters (AVWX)
–Tropical Cyclone Warnings and Condition of Readiness
–Recommendations
–Warnings and advisories
–High wind and seas
–Special weather advisories
–Local area warnings.
–Maritime OPAREA Forecasts
–Local Area and Port Forecasts
–Operational Weather Briefs
–Maritime Operations


