19 Cosmology Flashcards
(17 cards)
Which of the following is NOT evidence that supports the Big Bang Theory
A. Variation in gravitational field strength
B. The red-shift observed in light reaching Earth from distant galaxies.
C. Cosmic microwaves background radiation.
A. Variation in gravitational field strength
In general, the further away a galaxy is….
A. the smaller the observed increase in the wavelength of its light.
B. the slower it is moving away from us.
C. the bigger the observed increase in wavelength of its light.
C. the bigger the observed increase in wavelength of its light.
Below is a description of how the universe started…
1) initially, all the matter in the universe occupied a single point
2) This tiny space was very dense and very hot
3) This single spot then exploded
4) Space started expanding, and the expansion is still going.
What is stage 3 called?
The Big Bang
What is cosmic microwave background (CMB) radiation believed to be?
A. Energy from exploding supernovae.
B. Radiation given out by man-made objects in space, such as satellites and telescopes.
C. Leftover energy from the Big Bang explosion.
C. Leftover energy from the Big Bang explosion.
Light from galaxies is red-shifted. What do measurements of the red-shift tell us?
A. All galaxies are moving away from us at the same speed
B. More distant galaxies are moving away faster than closer galaxies
C. Closer galaxies are moving away faster than distant galaxies.
B. More distant galaxies are moving away faster than closer galaxies
What is CMB or cosmic microwave background radiation?
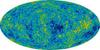
It is the left over energy of the Big Bang.
Wavelength of light is commonly stated in nanometers.
What does the prefix nano represent?
e.g. 450 nm
450 nm = 450 x 10-9 m
You need to be able to make calculations involving red-shift.
How is the amount the light from a galaxy is red-shifted (change in wavelength) related to the velocity of the galaxy?
This equation can be rearranged to find any of the variables.

According to the Big Bang theory, when the universe began it was…
A. small, dense and hot.
B. identical to the current universe
C. much larger and cooler than the current universe.
A. small, dense and hot.
Explain how red-shift provides evidence that the universe is expanding

- red-shift suggests that the galaxy is moving away from us
- red-shift measurements indicate that distant galaxies are moving away from us in all directions
- more distant galaxies have greater red-shifts than closer galaxies. indicating that they are moving away faster than closer galaxies
- this indicates that they whole universe is expanding.
Different elements (such as hydrogen) absorb different frequencies of light.
When light, formed at the centre of star, passes through an outer atmosphere of hydrogen, a pattern of dark lines is produced.
These lines are found at exactly the same position that the hydrogen absorb.
What happens to these lines if the galaxy or star producing the light are moving away from us?
All the lines are shifted (the same amount) towards the red end of the spectrum - they are red-shifted.

An observer measures the frequency of a passing ambulance’s siren with an oscilloscope. After the ambulance passes the observer, a decrease in the siren’s frequency is recorded. Name the effect that causes this change in frequency and explain why it happens.
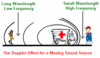
Name of the effect: Doppler effect
Explanation: The relative motion of the ambulance away from the observer stretches the wavelength of the sound waves, which lowers their frequency.
Different elements (such as hydrogen) absorb different frequencies of light.
When light, formed at the centre of star, passes through an outer atmosphere of hydrogen, a pattern of dark lines is produced.
These lines are found at exactly the same position that the hydrogen absorb.
What happens to these lines if the galaxy or star producing the light are moving towards from us?
All the lines are shifted (the same amount) towards the blue end of the spectrum - they are blue-shifted.

Why is the intense energy/light from the Big Bang that we now see all around us (Cosmic Microwave Radiation) in the microwave region of the spectrum?
After the Big Bang the energy was released in all direction and has cooled. The expansion of the universe since then means that this energy (light) has been red-shifted so far down the red end of the spectrum that it is now in the microwave region.

Some of out local galaxies are blue-shifted. What does this mean?
These local galaxies have a relative motion which is towards us
How is an expanding balloon with galaxies drawn on it a good analogy for what is happening to our universe?
Why is it a bad analogy?

Good analogy-
1) As you blow up the balloon, it stretches and the galaxies move further away from each other
2) the balloon represents the universe, as time goes on, space stretches and expands, moving the galaxies away from each other
Bad analogy-
1) the balloon only stretches so far
2) there would be galaxies inside the balloon as well
Which process releases energy in stars?
A. Combustion
B. Nuclear fission
C. Nuclear fusion
C. Nuclear Fusion
This occurs in the core of a star which is at more than 15 million Kelvin.


