2 - Protein and Amino Acid Metabolism Flashcards
(29 cards)
What are the major nitrogen containing compounds?
- Amino acids
- Proteins
- Purines and pyrimidines (DNA/RNA)
- Small amounts in others (e.g. haem, creatine phosphate, neurotransmitters, hormones)
What is creatinine and how is it used clinically?
A breakdown product of creatine and creatine phosphate. Usually produced at a constant rate and filtered into the urine.
Used as a clinical marker to estimate muscle mass (measure creatinine excretion over 24 hrs). Also used as an indicator of renal function.
- How is nitrogen brought into the body?
- Where is nitrogen stored within the body?
- Where is nitrogen excreted from the body?
- Nitrogen intake comes from dietary protein
- Nitrogen is stored in body protein, the amino acid pool and other nitrogen-containing compounds
- Nitrogen is excreted through waste products in faeces and urine and through loss of skin, hair and nails

Normal nitrogen balance is when N intake = N output. What causes positive or negative N balance?
- Positive - Intake > Output - increase in body protein. Normal state in growth, pregnancy or when recovering from malnutrition
- Negative - Intake < Output - loss of body protein. Never normal - commonly trauma, infection or malnutrition
Describe the process of protein breakdown in the body.
- Dietary protein is digested into free amino acids
- The amino group is converted to urea and excreted in the urine
- The carbon skeleton is broken down into glucose and ketone bodies
Give one example of:
- A glucogenic amino acid
- A ketogenic amino acid
- An amino acid that’s both glucogenic and ketogenic
- Glucogenic - Alanine
- Ketogenic - Lysine
- Glucogenic and ketogenic - Tryptophan

Decribe the hormonal control of protein synthesis and degradation.
- Insulin and growth hormone increase protein synthesis and decrease protein degradation
- Glucocorticoids (e.g. cortisol) decrease protein synthesis and increase protein degradation

What is the effect on protein reserves of Cushing’s syndrome?
Excess cortisol causes excessive protein breakdown. This weakens the skin structure leading to striae (stretch marks).
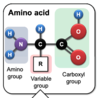
What are the three groups of an amino acid?
Amino group
Carboxyl group
R group
Give an example of an essential amino acid.
Isoleucine

In children and pregnant women there are three further essential amino acids. What are they and why are they necessary?
Arginine, tyrosine and cysteine
Required due to the high rate of protein synthesis
When non-essential amino acids are synthesised by the body where do the following come from?
- carbon atoms
- amino groups
- Carbon atoms - intermediates of glycolysis, pentose phosphate pathway, krebs cycle
- Amino groups - provided by other amino acids by transamination or from ammonia
Give some examples of some non-protein nitrogen-containing compounds.
- Catecholamines
- Glutathione
- Serotonin
- Histamine
- GABA
- Purines
- Haem
What two pathways remove nitrogen from amino acids?
Transamination
Deamination
What are the two key aminotransferases involved in transamination and how do they differ?
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT)
Converts alanine to glutamate (and alpha-ketoglutarate to keto acid)
Aspartate aminotransferase (AST)
Converts glutamate to aspartate (and oxaloacetate to keto acid)
A derivative of which vitamin is required for all aminotransferases?
Vitamin B6
Plasma ALT and AST are measured as part of …….. ………… …………
Levels are particularly high in what conditions?
Liver function tests
- Viral hepatitis
- Autoimmune liver diseases
- Toxic injury (e.g. death cap muschrooms)
What is deamination? Give an example of an enzyme that performs this process.
- Amino group is converted into free ammonia (toxic so converted to urea) in the liver and kidney. Remaining keto acids can be used for energy
- Performed by: amino acid oxidases, glutaminase, glutamate dehydrogenase
Describe the basic concepts of the urea cycle.
- Occurs in the liver and uses 5 enzymes
- Regulated based on demand for disposal of ammonia
- High protein diet induces enzyme levels
- Low protein diet or starvation represses levels

What is refeeding syndrome and when might this occur? How is this avoided?
- Ammonia toxicity when nutritional support is given to severely malnourished patients, as the urea cycle has been downregulated
- Risk if BMI < 16, unintentional weight loss of >15% in 3-6 months or 10+ days with little nutritional intake
- Refeed gradually at 5-10 kcal/kg/day
There are some autosomal recessive disorders caused by defects in enzymes of the urea cycle. What can these lead to?
- Hyperammonaemia
- Accumulation/excretion of urea cycle intermediates
How might ammonia toxicity present clinically and how is it managed?
- Vomiting, lethargy, irritability, mental retardation, seizures, coma
- Severe disorders show symptoms within one day of birth. Mild disorders may not present until early childhood
- Managed with low protein diet and replacing amino acids in the diet with keto acids
Describe some of the toxic effects of ammonia.
- Readily diffusible and highly toxic
- Interferes with amino acid transport and protein synthesis
- Disrupts cerebral blood flow
- Alkaline - pH effects
- Interferes with excitatory amino acid neurotransmitters (e.g. glutamate)
- Interferes with the TCA cycle
By what two ways is nitrogen in amino acids safely transported to the liver?
- Glutamine
- Ammonia combined with glutamate, cleaved back in the liver by glutaminase and ammonia is fed into the urea cycle
- Alanine
- Amine groups transferred to glutamate by transamination. Pyruvate is then transaminated by glutamate to form alanine
- Reversed in the liver and pyruvate used to make glucose