2018 Science T01W04 Flashcards
(37 cards)
Describe the structure of bacteria.
All bacteria have a rigid cell wall and contain all their DNA needed to make copies of themselves.

Describe the structure of a virus.
All viruses have a Protein coat (many of which are spiky) and contain some DNA.

How do bacteria reproduce?
Bacteria reproduce by making copies of themselves and dividing into two, identical ‘daughter’ cells

How do virus reproduce?
Viruses are ‘moochers’ – they reproduce by attaching themselves to host cells, injecting those cells with genetic information and using their parts to copy that genetic information so that more viruses are created.
Put simply, attaching to a host cell and turning it into a virus factory.

What is a virus?
A virus is a small, infectious agent that replicates only on the inside of living cells of other organisms.

What is bacteria?
Bacteria are single-celled micro-organisms that can exist either as independent (free-living) organisms or as parasites (dependent on other organisms for life).

Draw and label the structure of bacteria.

What happens when you get a vaccination?
Vaccination is considered the most effective method of preventing diseases. ‘Dead’ viruses are injected into a person to stimulate their immune system to build up a resistance against that disease.

How was Edward Jenner?
Edward Jenner, FRS was an English physician and scientist who was the pioneer of smallpox vaccine, the world’s first vaccine.

Bacteria differ from viruses because of?
Size, structure and they way they reproduce.

What do you call the way bacteria reproduces?
Mitosis.

Infectious diseases are caused by?
Microbes.

Two major types of microbes that cause infection are?
Bacteria and virus.

What are the smallest of all the microbes?
Virus.

How long can a virus live outside a host?
Seconds to minutes.

Do all bacteria cause infection?
No.

If temperature and nutrition allow, how quickly can bacteria multiply?
After 20 minutes.

Common symptoms of a viral or bacterial infection are?
Fever, fatigue and general malaise (a general feeling of discomfort, illness, or unease whose exact cause is difficult to identify).

An antibiotic is only effective against?
Bacterial infections.

What plays an important role in prevention of microbial infections?
Good hygiene.

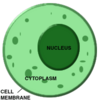
What is a Plasma membrane?
The outermost border of a bacteria.

What is a cell wall?
A protective layer of the cell that protects its organelles (tiny cellular structures that performs specific functions within a cell).

What is Cytoplasm?
Fluid that suspends the organelles within the bacterial cell.
How do Bacteria move?
Thin fibers responsible for movement are called flagellum.















