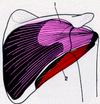
Shoulder Muscles Flashcards

Anterior Deltoid (1, Pink)
Coracobrachialis (2, Red)
Anterior Deltoid Origin
(Pink)

Anterior and lateral 1/3 of the clavicle
Anterior Deltoid Insertion
(Pink)

Deltoid tuberosity
Anterior Deltoid Action
(Pink)

Flexion, internal rotation and horizontal adduction of the shoulder
Coracobrachialis Origin
(Red)

Coracoid process of the scapula
Coracobrachialis Insertion
(Red)

Medial surface of the humerus opposite of the insertion of the deltoid
Coracobrachialis Action
(Red)

Flexion and adduction of the shoulder

Pectoralis Major
Pectoralis Major Origin

Medial 1/2 of the clavicle, sternum and cartilage of 1-6 ribs
Pectoralis Major Insertion

crest of the greater tuberosity of the humerus
Red Muscle

Biceps Brachii
Biceps Brachii Origin
(Red)

Coracoid process of the scapula and the supraglenoid tubercle of the scapula
Biceps Brachii Insertion
(Red)

Tuberosity of the radius and the bicipital aponeurosis
Biceps Brachii Action
(Red)

Elbow Flexion, shoulder flexion and forearm supination
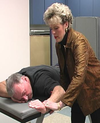
Testing Position for Shoulder Flexion
Against Gravity - Sitting, patient assumes a position of 90o of shoulder flexion. Therapist resists on the distal end of the humerus in a downward direction toward extension.
Gravity Eliminated – Sidelying with the arm supported by the therapist, patient assumes a position of 90o of shoulder flexion. Resistance is applied to the distal end of the humerus in a parallel direction toward extension.
*The anterior deltoid is the primary shoulder flexor of the above mentioned muscles. They function as a group to produce shoulder flexion although each of the above muscles also functions to produce other movements. The coracobrachialis, pectoralis major and the biceps brachii are considered accessory muscle movers. The primary function/action of each of the above muscles is bolded.


Latissimus Dorsi (1, Pink)
Teres Major (2, Red)
Latissimus Dorsi Origin
(Pink)

Spinous process of T7-T12, spinous process of the lumbar vertebra, sacrum to the posterior iliac crest as well as to ribs 7-10 and to the inferior angle of the scapula
Latissimus Dorsi Insertion
(Pink)

Distal to the lesser tuberosity (located on anterior surface of humerus)
Latissimus Dorsi Action
(Pink)

Scapular depression, Extension, internal rotation, and adduction of the shoulder
Teres Major Origin
(Red)

Lower 1/3 of the lateral border of the scapula to the inferior angle
Teres Major Insertion
(Red)

Distal to the lesser tuberosity of the humerus
Teres Major Action
(Red)

Extension, internal rotation and adduction of the shoulder

Posterior Deltoid (A – Red)
Triceps (G, Pink)
Posterior Deltoid Origin
(Red)

Spine of the scapula
Posterior Deltoid Insertion
(Red)

Deltoid tuberosity
Posterior Deltoid Action
(Red)

Horizontal Abduction, extension, and external rotation of the shoulder
Triceps Brachii Origin
(Pink-G)

Infraglenoid tubercle of the scapula, inferior to the neck of the humerus, and the lower 1/2 of the posterior surface of the humerus