2.4-2.5 Flashcards
(77 cards)
A 66 block is a
punch down block used to connect individual copper wires together. Primarily for telephone applications.
110 blocks are used primarily for
telephone applications in high-speed networks because the introduce less crosstalk.
Patch panel is a mounted hardware assembly that…
contains ports used to connect and manage incoming and outgoing LAN cables.
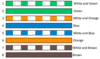
T568A Pinout Order
Pin 1: GW = White with green stripe
Pin 2: G = Green Pin
3: OW = White with orange stripe
Pin 4: B = Blue Pin
5: BW = White with blue stripe Pin
6: O = Orange
Pin 7: BrW = White with brown stripe
Pin 8: Br = Brown
fiber distribution panel
A patch panel for fiber optic cabling is called a
The smart jack is a way for your (WAN) provider to perform
some additional troubleshooting functions without having to visit your location.
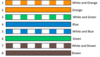
T568B Pinout Order
Pin 1: OW = White with orange stripe
Pin 2: O = Orange
Pin 3: GW = White with green stripe
Pin 4: B = Blue
Pin 5: BW = White with blue stripe
Pin 6: G = Green
Pin 7: BrW = White with brown stripe
Pin 8: Br = Brown
What are some functions that Smart Jacks Allow (WAN) Providers to perform? (2)
- Set up a loopback
- Provide diagnostics remotely

T568A
When organizing an MDF or IDF make sure to record names in
tables and diagrams.

T568B
When organizing an MDF or IDF develop a naming convention and use it to label (5)
- Cables
- Racks
- Wall jacks
- Patch panel ports
- Network devices
When organizing an MDF or IDF document these four facts about the cable details attached: (4)
LIL G
- Location
- Installation dates
- Lengths
- Grade (Cable Grade)
When organizing an MDF or IDF Consider using
cable management software

A crimping tool is used to attach connectors to wires. Some are designed for power connections.
Punch down tool
Forces wire into a wiring block
Optical Time Domain Reflectometer (TDR / OTDR) (4)
Performs the same function as a TDR, but is used for fiber optic cables.
- Measures signal loss
- Creates wire maps.
- Estimates fiber lengths
- Determines light reflection
How do OTDR’s work
sends light pulses into the fiber cable and measures the light that is scattered or reflected back to the device.
A multimeter tests (3)
- AC/DC voltages
- Continuity
- Wire mapping

A Tone Probe/Generator can be used to
trace and identify cables or wires within a group by sending an analog sound through the wire
A cable tester (3) main functions
- Can identify Missing pins
- Can identify Crossed wires
- Verifies that the cable can carry a signal from one end to the other
****Not generally used for frequency testing
cable tester can be used to quickly tell the difference between
a crossover and a straight-through cable..
A Loopback adapter (lookback plug) (2)
- Used to verify that a device can both send and receive signals.
- reflects a signal from the transmit port on a device to the receive port on the same device.
A spectrum analyzer
measures the magnitude of an input signal versus frequency