Sex hormones and disease Flashcards
Briefly describe the release and regulation of sex hormones?
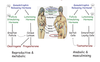
Describe the synthesis of the sex hormones?

Which enzymes are potential targets in the synthesis of sex hormones?
Aromatase (testosterone > oestradiol and androstenedione > oestrone)
5a reductase (testosterone > dihydrotestosterone)

Describe the clinical uses of oestrogens?
Children: hypogonadism
Adults: primary amenorrhoea, contraception, menopause
Describe the benefits and risks associated with postmenopausal hormone therapy?
BENEFITS
Improved bone density
Relief from flushes, fatigue and vaginal dryness
Reverses atrophy of vulva, vagina and urethra
Improved sleep
Reduced incidence of colorectal cancers
Reduced CHD incidence
Possible reduced incidence of Alzheimer’s
RISKS
Breast tenderness, nausea, fluid retention
Increased risk breast and uterine cancer
Increased risk of thromboembolism/stroke
How do the benefits and risks of postmenopausal hormone therapy weigh up?
Benefits believed to outweigh risks
Describe the mechanism of action of oestrogen?
Cross membrane > activates cytoplamic receptors > homodimers formed > homodimers interact with EREs in nucleus > gene activation/repression
Potential to form heterodimers with different transcription factors > activate signalling in different ways
Receptor may be located on the membrane > fast actions

Why are some of the actions of oestrogen rapid, whilst others are slower?
Fast actions as a result of binding membrane receptors
Slower actions associated with intracellular receptors
Describe different ways in which the signalling of oestrogen may be altered?
Different receptor location
Interaction with different transcription factors
Different receptor subtypes
Describe how oestrogen is thought to be involved with breast cancer?
Binding to ER stimulates growth
Binding to ER also switches on progesteron receptor > growth and differentiation

Describe the ER and PR receptor levels in breast cancer?
Pre-menopausal: 60-65% ER/PR +ve
Post-menopausal: 70-75% ER/PR +ve
What are SERMs?
What are they used for?
Selective oestrogen receptor modulators
Oestrogen blockade > application in breast cancer

What is tamoxifen and what is it used for?
Partial agonist at oestrogen receptors
Palliative treatment of metastatic breast cancer
Adjuvant after lumpectomy
Describe the adverse effects of tamoxifen?
Endometrial hyperplasia, polyps and cancer
Thromboembolic events
Thrombocytopenia
Ocular toxicity
Menopausal symtpoms
Resistance > tumours may recur
What is exemestane?
What is it used for?
Aromatase inhibitor
Decrease oestrogen production > inhbit receptor activation > applications in breast cancer to improve disease free survival after tamoxifen




