2nd Year Books Flashcards
(212 cards)
What level does the isthmus of the thyroid lie?
Lies opposit the 2nd - 4th tracheal rings
How are the suprarenal glands peritonised?
They are retroperitoneal
What exists within the free border of the falciform ligament?
Round ligament
Paraumbilical veins
What vertebral level are renal veins given off at?
L1 - L2
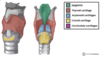
What is the level of the thyroid?
C5 - T1
Lies between the 6th tracheal ring and the thyroid cartilage
What is the terminal group of lymph nodes for the head and neck?
The deep cervical nodes - they are found surrounding the internal jugular vein and are contained within the carotid sheath
At the inferior end of the deep cervical chain of lymph nodes, the efferent lymphatic vessels join together to form the jugular lymph trunk on each side
Aneurysms in what artery result in palsy of the third cranial nerve?
Posterior cerebral artery
With what two areas does the cavity of the middle ear communicate?
Tympanic cavity - nasal cavity via eustachian tube
Mastoid antrum via air cells
Which veins of the stomach drain into the hepatic portal vein, which ones don’t?
Right and left gastric veins drain into the hepatic portal vein
Left and right gastro omental veins ultimately drain into the superior mesenteric veins
Where does the septum pellucidum project to?
Superiorly = corpus callosum
Inferiorly = fornix
Poseriorly = interventricular foramen
Where do the superior thyroid artery and inferior thyroid artery come from?
Superior - branch of ECA
Inferior thyroid artery - subclavian artery?
What are the branches of the ECA
Some Anatomists Like Freaking Out Poor Medical Students
Superior thyroid
Ascending pharyngeal
Lingual
Facial
Occipital
Posterior auricular
Maxillary
Superficial temporal
What is the funcion of the tensor tympani?
Tenses the tympanic membrane
What is the fornix?
A bundle of fibres that links the hippocampus with the mamillary bodies of the hypothalamus
SADPUCKER
Suprarenal glands
Aorta/IVC
Duodenum 2nd and 3rd parts
Pancreas (except the tail)
Ureters
Colon (ascending and descending(
Kidneys
Oesophagus
Rectum
Which branch of the renal artery supplies the nephron?
Interlobular branches
What do the tracheal nodes drain and where do you find them?
Drain the trachea and the thyroid gland - found around the trachea
What structures pass through the cavernous sinus?
Oculomotor
Trochlear
Abducent
Opthalmic
Maxillary
Internal carotid
What part of the brain lies immediately superior to the midbrain?
Thalamus
What is contained within the diencephalon?
The hypothalamus, thalamus and pineal gland
Which 4 bones form the pterion?
Frontal
Temporal
Parietal
Sphenoid
What ioens into the sphenoethmoid recess?
Sphenoid sinus
Into which vein does the suprarenal vein drain into?
RHS = IVC
LHS = Renal vein
Which strutures pass through the parotid?
Facial nerve
Retromandibular vein
ECA