Alleles (T3) Flashcards
What are alleles?
Characteristics such as eye colour are controlled by a single gene. These genes have alternative forms knows as alleles. Eg: the gene which codes for eye colour has an allele which codes for blue eye colour as well as an allele which codes for brown eye colour.

Explain, with examples, the function and outcomes of the dominant and recessive alleles..
The characteristic which is controlled by a dominant allele always develops in the offspring if the allele is present in one or both of the chromosomes in a pair. The characteristic which is controlled by a recessive allele only develops in the offspring if the recessive allele is present in both of the chromosomes in a pair. Eg: if the allele for brown eyes is dominant and the allele for blue eyes is recessive, then an individual who inherits one or two alleles for brown eyes will have brown eyes, while a person will only have blue eye if they inherit two copies of the allele for blue eyes.

What are homozygous alleles?
Alleles which are the same
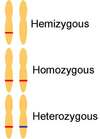
What are heterozygous alleles?
Alleles which are different

What does ‘co-dominance’ mean with regards to alleles and inheritance? Give an example.
This is when both alleles are expressed in the heterozygous situation. Eg: the blood grouping system. This is based on the presence of surface proteins of red blood cells. Individuals who are blood type AB are heterozygous, with one allele for protein A and one allele for protein B. In this situation both alleles are expressed and the red blood cells possess both proteins.