3rd week Flashcards
(87 cards)
Go through shoulder examination
- IIIQAG: can dress self w/o diffiulty, can wash own hair
- Inspect: from the front, side, back
- Palpation: temperature, bones, muscles
- Active movement: screening [hands behind head/back] flexion, extension, lateral flexion, IR/ER
- Passive movement: with hand on shoulder the same as above
- Special tests: painful arc, scarf test, ER AR, lift off test, empty can AR
- Completion: neurovascular status of the UL, C-spine and elbow
Go through elbow examination
- IIIQAC
- Inspect arms loosely by their sides
- Palpation: temperature, radial head, medial/lateral epicondyles and olecranon prcoess for tenderness
- Active ROM: flexion/extension/pronation/supination
- Passive ROM: same as above whilst feeling for crepitus
- Function: can pt move hand to their mouth/nose, check both sides
- Special tests: golfer’s elbow [supinated position, ask pt to make fist and flex their wrist AR], tennis elbow [pronated position, ask pt to extend wrist AR, will cause pain lateral epicondyl]
- Completion: neurovascular status UL, ipsilateral shouder and wrist/hand
Go through ankle/foot examination
1.
Go through spine examination
1.
Go through hand examination
1.
Go through GALS examination
1.
Go through RESP exam
1.
Go through GASTRO exam
1.
Go through CARDIO exam
1,
XR findings for a patient with RA
- Periarticular erosions: synovitis erodes bone causing the formation of cysts
- Periarticular osteopenia: loss of bone density occurs as a result of disuse due to pain and secondary effects of steroids
- Soft-tissue swelling: subtle widening of the joint space may be seen when synovitis is mild. Severe synovitis is seen as gross swelling around the joints
- Joint subluxation and malalignment: as ligaments become dysfunctional and joint sublux and can even dislocate. This gives rise to the classic deformities hands/feet
XR findings for a patient with OA [4]
- loss of alignment [varus]
- loss of joint space
- subchondral sclerosis
- subchrondral cyst
- osteophytes
LOSS [ignore varus]
Which joints does OA typically affect? [2]
Typically affects large synovial joints including hip, knee, rst metatarsophalangeal joint of the foot, facet joints of the spine, shoulder and elbow. In the hand the interphalangeal joints and carpometacarpal joint at the base of the thumb may be affected.
What is Felty’s syndrome? [1]
Combination of RA, splenomegaly and neutropenia
Where do immune complexes typically present in RA patients? [1]
Called rheumatoid nodules, they mainly affect the extensor surfaces
When would an XR vs a CT vs a MRI vs USS be indicated in orthopaedics? [4]
- XR: arthritis, fractures, chest
- CT: complex fractures [spine, tibial, platuea, pilon, pelvis]
- MRI: spinal disc prolapse, ligamentous or meniscal injury, OM
US: tendon rupture, foreign bodies, ‘FAST’ in trauma
What is the most common cause of OM/septic arthritis in children? [2]
Acute haematogenous osteomyelitis:
- organisms escape from vessels in the physis where blood flow is slowest. An abscess occurs in the metaphysis
- pus ascapes under adjacent periosteum, elevation of the periosteum can be seen XR
- in children, hip/ankle/wrist and shoulder have intra-articular physis allowing organisms to enter the joint and cause septic arthritis
Carpal bone mnemonic
Some - scaphoid
Lovers - lunate
Try - triquetrium
Positions - pisiform
They - trapezium
Can’t - capitate
Handle - hamate
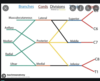
Go through the brachial plexus
Knee anatomy
Hip examination
awq
What are the different types of laxatvies?
a
What is the COACHES [I think?] criteria for septic arthritis?
Features of Perthes disease
a
Features of SUFC
a





















