4/12 Upper Extremity Injuries - Corbett Flashcards
(25 cards)
brachial plexus
mnemonic
robert taylor drinks cold beer
roots-trunks-divisions-cords-branch
- roots of spinal nerves
- trunks in posterior triangle of neck
- divisions behind clavicle
- cords in axilla
lateral cord →
- musculocutaneous n
- lat pectoral n
- lat root of median n
medial cord →
- medial cutaneous n of arm
- medial pectoral n
- medial cutaneous n of forearm
- medial root of median n
- ulnar nerve
posterior cord →
- axillary n
- upper and lower subscapular nn
- thoracodorsal n
- radial n



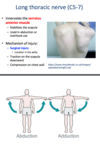
long thoracic nerve
C5-C7
innervates: serratus ant m
- stabilizes scapula
- abduction/overhead use (arms all the way up)
mech of injury:
- surgical (in axilla)
- downward traction on scapula
- chest wall compression
presentation: winged scapula
axillary nerve
C5-C6
innervates: deltoid
- major ABductor at shoulder
innervates: teres minor (clinically irrelevant)
sensory: skin over deltoid
mech of injury: shoulder dislocation (fall with shoulder abducted/externally rotated), fracture of surgical neck of humerus

musculocutaneous nerve
C5, C6, C7 (from lateral cord of BP)
- pierces coracobrachialis…
-
innervates:
- biceps brachii
- brachialis
- coracobrachialis
- and then continues as lateral cutaneous nerve of arm

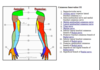
radial nerve
C5-T1
innervates: posterior muscles of arm/forearm
- extension at elbow
- extension of wrist/fingers
- supination of forearm
sensory: posterior arm/forearm, posterior hand (lateral 3.5 digits
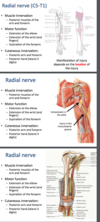
mech of radial nerve injury

median nerve
C5-T1
innervates:
- (almost all) muscles of forearm
- muscles of thenar eminence
- 1st, 2nd lumbricals
wrist flexion and abduction, forearm promation, thumb flexion and opposition, flexion of digits 2/3
sensory: palmar surface of hand
median nerve injuries/deficits
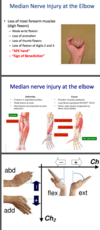
normal position of thumb
muscles involved
deficiency
LOAF
- abductor pollicis brevis and opponens pollicis keep thumb in slightly ventral and abducted
passive sign - pt not DOING anything to show this sign

sign of benediction
active sign - need to ask pts to make a fist

proximal median nerve injury
vs
distal median nerve injury
sign of benediction (active sign)
vs
median clawing (passive sign)

mechanisms of median nerve injury

carpal tunnel syndrome
palmar branch of median nerve comes OFF BEFORE carpal tunnel!!!

ulnar nerve
C8-T1 (from medial cord)
- no branches in axilla, arm
- passes behind medial epicondyle to enter forearm
innervates: 1.5 muscles in forearm
- flexor carpi ulnaris → wrist flexion on ulnar side
- flexor digitorum profundus → flexion of distal phalanx of digits 4/5
most of the stuff in teh hand:
- hypothenar muscles
- meial two lumbricals
- adductor policis
- all interossei
sensory__:
- dorsal cutaneous branch
- palmar cutaneous branch
claw hand

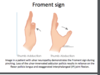
Froment sign
ulnar nerve injury
hyperflexion of thumb when making a-ok pinch sign
loss of ulnar-adductor pollicis = reliance on flexor pollicis longus and exaggerated IP joint flexion
ulnar injuries
claw hand
- paralysis of hypothenar and interosseus muscles
- loss of adductor policis and medial 2 lumbricals
- see:
- hyperext of MCP jts
- flexion of IP joints (obv in 4th, 5th digits)
- inability to abduct or adduct the fingers
“ulnar paradox”
proximal ulnar nerve injury = “not as bad” claw hand
- hyperextension at MCP joints
- flexion of IP joints (bc FDS still intact → not as bad as it would be if FDP was lost too)
- loss of abduction and adduction

hamate
hook of hamate can fracture if palm hits a surface → damage to deep branch of ulnar n
- wasting of adductor pollicis, 1st dorsal interossei
review images

upper brachial plexus injury
lower brachial plexus injury
upper → “Erb-Duchenne palsy” → “waiter’s tip”
lower → “clawhand”

Erb Duchenne palsy
upper BP injury
results from excessive displacement of head to opposite side/depression of shoulder on same side
(i. e. formation of an obtuse angle between head/shoulder)
ex. labor, surgical positioning, fall
affects C5/C6 roots of superior trunk (see pic)
**link to Horner syndrome bc sympathetic trunk runs close




