4-4 Stroke Flashcards
(69 cards)
How frequent is stroke? How often is it deadly?
- Third leading cause of death in the US (~6% of all deaths)
- Incidence of strokes is 795K a year in the US (180K of them are recurrent strokes)
–1 stroke every 40 seconds in average
- Prevalence—6.5 mln people with h/o stroke
- Death rates from strokes per 100,000
–44.7–for white males
–70.5 for black males
–44.0 for white females
–60.7 for black females
What is the leading cause of long-term disability in the US?
stroke
What is the mortality after a stroke?
•Mortality after strokes—14-27% depending on age/gender/race
What is the cost of stroke in the US?
- The estimated direct and indirect cost of stroke for 2009 is $68.9 billion.
- The mean lifetime cost of ischemic stroke in the United States is estimated at $140,048.
What is a CVA?
- Cerebrovascular Accident (C.V.A.)
- Abrupt onset of a neurological deficit that is attributable to a focal vascular cause
What are the 2 major types of stroke? What is the relative prevalence of each?
•2 major types of stroke:
–Hemorrhagic stroke (caused by cerebral hemorrhage )
•15% of all strokes
–Ischemic stroke (caused by cerebral ischemia)
•85% of all strokes
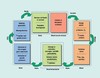
Describe the ischemic cascade in terms of neurons, cell injury, and severity.

Describe the cascade of bad that happens following a vascular infarct in the brain, over the course of seconds - minutes - hours - days - weeks.
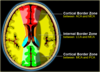
What is a ‘penumbra’?
•Brain tissue surrounding the cerebral necrosis that exhibit reversible ischemic changes

Name some causes of ischemic stroke under an embolism etiology.
Causes of Ischemic Stroke
Embolism:
Arterial: Carotid or Aorta
Heart: Atrial Source, Ventricular Source, or Valvular Lesions
Paradoxical Emboli
Name some causes of ischemic stroke that do not fall under an etiology of large artery thrombosis, embolism, or lacunar cause.
Causes of Ischemic Stroke, “Other” Category:
Watershed infarcts
Hypercoagulable disorders
Vasculitis
Vasospasm
Dissection of Artery
How do large artery thrombosis occur?

What are the types of emboli?
Type dependent on origin:
–Originating from an atherosclerotic plaque
–Originating from thrombus
What are the main sources of emboli?
•Source of emboli
–Heart
–Artery to artery
–Lower extremity DVT with paradoxical emboli
What are some atrial sources of cardiac emboli?
–Atrial Fibrillation/Flutter
–Atrial septal aneurism
–Atrial tumors (myxoma)
How does a-fib lead to thrombus formation?
•Fast and ineffective atrial contraction leading to stasis and thrombus formation

What is an atrial septal aneurism?
•Weakening and out-pouching of interatrial septum, leading to stasis and thrombus formation (mural)
How are atrial septal aneurisms classified?
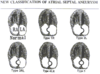
How do atrial myxomas contribute to embolus?
- Pieces of tumor may tear off and become emboli
- Associated thrombus can embolize artery down the stream
What are some ventricular sources of cardiac emboli?
–Cardiomyopathy
–Myocardial Infarction
–Ventricular aneurisms
How does cardiomyopathy contribute to emboli?
•Weak and dilated ventricle isn’t pumping efficiently leading to blood stasis and thrombus formation
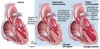
How does MI lead to emboli formation?
•Part of the wall is not moving creating stasis and leading to mural thrombosis
What are 7 valvular sources of cardiac emboli?
•Valvular source
–Rheumatic mitral stenosis
–Prosthetic valves
–Infective and non-infective endocarditis
–Nonbacterial thrombotic (marantic) endocarditis associated with malignancies and prothrombic states
–Calcification of valves
–Bicuspid aortic valves
–Inflammatory valvulitis (i.e., Libman-Sacks endocarditis, Behcet Disease, Syphilis)
What is an example of artery to artery embolic infarcts? What increases the risk of stroke in this instance?
•Carotid Artery atherosclerosis/stenosis
–Causes 5% of all strokes
–The tighter the stenosis the higher risk of stroke
–May cause embolic or thrombotic type of strokes