L4.2+4.3 Ab viscera Flashcards
1
Q
How is the abdominal quadrants divided?
A
- Horizontal line through umbilicus
- Vert line from sternum to pubic symphysis
2
Q
Esophagus
A
- Muscular tube, 25cm
- Conduct food from pharynx to stomhac via peristalsis
- Enters stomach from the L of side, into R side of somtach

3
Q
Esophogastric junction (Z-line)
A
- Changes from esophageal mucosa to gastric mucosa
- Stratified squamous epithelium → simple columnar epithelium)

4
Q
Esophageal narrowings
A
- Cervical: Upper esophageal sphincter
- Thoracic: Aortic arch & LMB
- Abdomen: Diaphragmatic orifice
5
Q
BS of the esophagus (ab part only)
A
- L gastric branch from aorta
6
Q
Venous drainage of the esophagus (ab part only)
A
- L gastric portal
7
Q
Herniation of the stomach
A
- Sliding hiatal hernia: Through esophagus
- Paraesophageal hernia: Next to esophagus

8
Q
Stomach
A
- LUQ, intraperitoneal
- J-shaped → have greater & lesser curvature
- Cardiac orifice (Prox opening of R border)
- Pyloric orifice (distal opening)
- Fundus (part that projects upwards above the cardio orifice - usually full of gas)
- Body
- Angular notch (on lesser surface where body ends - begins to funnel down)
- Pyloric antrum (funnel bit)
- Pylorus (converges on the most tubular & distal part)
- Has a pyloric sphincter - controls gastric outflow into duodenum
- Rugae (gastric folds in stomach - more predominant twd pylorus)

9
Q
Mesentery of the stomach
A
- Lesser omentum: Connected to under surface of liver on the lesser curvature of stomach
- Greater omentum: connects stomach to POS wall

10
Q
BS to the stomach
A
- Gastroepiploic vessels running along curvatures
11
Q
Duodenum
A
- Retroperitoneal (but 1st inch is intraperitoneal → hasn’t made it back to POS wall), 25cm
- C-shaped loop surrounding head of pancreas
- Site of digestion & absorption of digestive products
- Villi → ↑SA → ↑Abs

12
Q
Duodenum 1) Duodenal cap
A
- 5cm
- Upwards & backwards (adjacent to R.crus, overlying hilum of R. kidney)
- Ulcers tend to form (due to imbalance of gastric contents & acid)

13
Q
Duodenum 2) Descending vertical part
A
- 7.5cm
- Vertical descent on R.psoas next to head of pancreas
- Has transverse mesocolon (surrounds the transverse colon)
- Have pailla

14
Q
Duodenum 3) Horizontal part
A
- 10cm
- Has root of mesentery of SI
- R to L.psoas in front of IVC & aorta, at level of L3

15
Q
Duodenum 4) Ascending part
A
- DJ flexure
- Curves forward

16
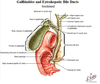
Q
Duodenal papilla
A
- On P-M wall 1/2 down of 2nd part of duodenum
- Major: where common bile duct & pancreatic duct enters
- Minor: position is higher than maj, where accessory pancreatic duct enters

17
Q
Jejunum + Ileum
A
- 4-6m
- Starts at DJ flexure
- 2/5 jejenum, 3/5 ileum