Nervous System - Peripheral Nervous System Flashcards
1
Q
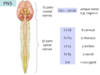
Peripheral Nervous System
A
- all of the nervous tissue outside of the CNS
- primarily consists of nerves that function to communicate between the body and the CNS
Cranial nerves - PNS nerves that connect to the brain
Spinal Nerves - PNS nerves that connect to the spinal cord
2
Q
Cranial Nerves
A
- allow direct communication between the body and the brain
- one exception - accessory nerve (CN XI) arises from the spinal cord
- 12 pairs (CN I - CN XII)
3
Q
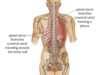
Spinal Nerves
A
- allow communication between the body and the spinal cord
- 31 pairs
- connected to the spinal cord by rootlets (dorsal root and ventral root)
- attached to spinal cord at regular intervals (reflection of segmental development)
8 Cervical
12 Thoracic
5 Lumbar
5 Sacral
1 Coccygeal
4
Q
Cranial Nerves and # Spinal Nerves

A
- 12 pairs cranial nerves
- 31 pairs spinal nerves
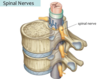
5
Q
Spinal Cord Segment
A
- each individual portion of the spinal cord that is derived from one somite (blocks of mesoderm that lead spinal cord to develop in segmental fashion)
- each spinal cord segment is associated with one spinal nerve pair (one nerve on right and one left)

6
Q
Somites
A
- derived from paraxial mesoderm
- repeating “blocks” of mesoderm that lie on either side of the neural tube
- develops into adult structures in a segmental pattern (i.e. vertebrae)
7
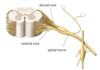
Q
Dorsal Root
A
- the posterior root (roots connect spinal nerves to spinal cord)
- sensory root - contains sensory neurons
- you’re “sensitive” when someone talks behind you “back”
8
Q
Ventral Root
A
- the anterior root (roots connect spinal nerves to spinal cord)
- motor root - contains motor neurons
- you drive a “motor” vehicle facing “front”

9
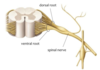
Q
Spinal Nerve
A
- collection of axons in the PNS
- connected to the spinal cord by rootlets (dorsal and ventral roots)
- divides into two branches (dorsal ramus and ventral ramus)
10
Q
Dorsal Ramus
A
- one of two primary branches of the spinal nerve
- innervates the muscles and the skin of the back

11
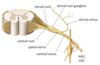
Q
Ventral Ramus
A
- one of two primary branches of the spinal nerve
- innervates structures of the ventrolateral neck/trunk and limbs (everything the dorsal does not)
- typical - travels around the body wall and innervates muscle and skin of the trunk
- atypical - forms nerves plesuses
12
Q
Dorsal Root Ganglion
A
- a collection of neuron cell bodies in the PNS
- enclosed by a connective tissue covering
- each dorsal root has a ganglion associated with it (dorsal root ganglion) - contains cell bodies for all the afferent neurons that travel in a particular spinal nerve and its dorsal root

13
Q
Cauda Equina
A
- collection of dorsal and ventral roots in the inferior portion of the dural sac that have not exited the vertebral canal through intervertebral foramina
- named for its resemblance to a “horses tail”

14
Q
Distribution of cranial vs. spinal nerves
A
Cranial nerves - primarily innervate structures in the head and neck
Exceptions - CN X (Vagus Nerve) travels to the lower abdomen
Spinal nerves - primarily innervate structures below the head
Exceptions - the first few cervical nerves do send some branches to the head

15
Q
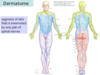
Dermatome
A
- the area of skin innervated by a particular spinal nerve pair
- due to segmental development from somites