GERD, esophageal cancer Flashcards
what physiology is occuring in body for GERD to occur
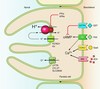
- lower esophageal sphincter TRANSIENTLY relaxes allowing back flow of stomach contents

what is the montreal classification of gerd
- a condition that develops when the reflux of stomach contents cause troublesome symptoms or complications
hallmark symptom of GERD
-
heartburn
- typically post-prandial
- regurgitation
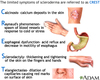
list the extraesophageal manifestations of GERD
- bronchospasm
- laryngitis/hoarsness
- chronic cough
- loss of dental enamel
Pt with GERD may experience what other symptoms
- chest pain, may mimick angina
- dysphagia (r/o stricture)
- hypersalivation
- globus sensation (lump in throat)
- odynophagia (painful swallowing)
- Nausea
What are some things that worsen GERD symptoms
- obestiy
- pregnancy
- gravity: encourgae pts to elevate head of bed
- medications
- foods
What class of medications used for osteoporosis can injury mucosa and worsen GERD symptoms
- bisphosphonates
- need to take with full glass of water
- don’t lay down for 30 min after taking med
what is a Hiatal hernia
- portion of the stomach enters above the diaphragm into the chest
what are the two types of hiatal hernias
- sliding hernia (most common)
- paraesophageal hernia

symptoms of hiatal hernia
- most asymptomatic
- can cause GERD
- heartburn, cough, hoarseness, CP
Barium swallow can not show what in the evaluation of GERD
- mucosal inflammation not seen
- can see hiatal hernia and strictures
what is the best diagnostic test to evaluate mucosal injury
EGD
What is the best study to confirm GERD but frequently not needed
ambulatory pH monitoring
ambulatory pH monitoring can do what is assessment of GERD
- quantify reflux and allow pt to log symptoms
function of Esophageal manometry
- measures the function of the LES and the pressures and pattern of muscle contractions (peristalsis) of the esophagus
how is GERD most frequently diagnosed
- clinically
- diagnostic studies and labs are not needed with classic history of GERD
Lifestyle and dietary modification education for pts with GERD
- adjustment of bed
- no food or drink within 3 hrs of bedtime
- weight loss
- food avoidance
- chocholate
- fried and fatty foods
- caffeine and soda
- red wine, alcohol
- citrus, tomatoes, onions
List the 3 medication options for GERD tx
- antacids :Tums
- H2 blockers (ranitidine)
- Proton pump inhibiters (prilosec)
function of antacids in tx of gerd
- neutralize gastric pH
- short lived benefit
- do not prevent GERD
function of H2 blockers in tx of GERD
-
block action of histamine at H2 receptors of the parietal cells of the stomach
- leads to decreased stomach acid

when should proton pump inhibitors be taken
take 30 minutes before breakfast