5 Hypertension and Heart Failure Flashcards
(39 cards)
How is hypertension defined? (NICE guidelines)
NICE Hypertension= BP >140/90 mmHg
Elevation in blood pressure that is asssociated with an increase in risk of some harm
Elevated blood pressure that treated will do more good than harm
What are the different types of hypertension? (4)
- Essential/primary/idiopathic
- Secondary (to other pathology eg Pheochromocytoma)
- Isolated systolic/diastolic
- White coat/clinic (elevation of blood pressure whilst at clinic)
- need to be careful to not overdiagnose

Outline the best practice for measuring blood pressure?
- Patient sat, relaxed, arm supported
- Take pressure from both arms
- If >15mmHg difference between arms, repeat measurement
- Use arm with higher reading
What might be classes as a hypertensive emergency? What are the clinical signs?
Hypertensive emergency= BP >180/120 + clinical signs

What BPs are classed as hypertension for:
- <80 year olds
- >80 year olds
- type 1 diabetics
- <80 year olds= 140/90
- >80 year olds= 150/90
- type 1 diabetics= 135/85
What are the different stages of hypertension (give BP values)

What is defined as prehypertension? What lifestyle changes should be recommended to patients who are prehypertensive?
Prehypertension= >120/80 and < 140/90 mmHg
- Promotion of regular exercise
- Healthy diet
- Limit/reduce alcohol intake
- Smoking cessation
- Reduce dietary sodium
- Discourage excessive caffeine consumption
What are the main therapeutic agents for treating primary hyertension? (4)
- ACE inhibitors (Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors)
- ARBs (Angiotensin receptor blockers
- CCBs (Calcium channel blockers)
- Diuretics (eg thiazides)
How do ACE inhibitors aim to reduce blood pressure? (ie what mechanisms)
Limit conversion of Angiotensin I to Angiotensin II
Reduce angiotensin II effects:
- Vasodilation
- Reduce aldosterone release (increase Na+ and H2O excretion)
- Reduce ADH (vasopressin) release (increase H2O excretion)
- Reduce cell growth and proliferation

Can angiotensin II be produced from angiotensin I independently of ACE?
Yes- by chymases

Give the names of 2 ACE inhibitors.
naproxen= NSAID

Explain why a patient may get a dry cough as a result of taking lisinopril or ramipril.
- Bradykinin is a substrate for ACE aswell as ACEi.
- Use of ACEi potentiates bradykinin
- Bradykinin causes vasodilation via NOS/NO and prostacyclin (vasodilator)
- Dry cough due to build up of bradykinin
What are some of the contraindications of ACE inhibitors? (5) Who should they not be given to? (3)
Contraindications
- Hypotension
- Dry cough
- Hyperkalaemia (low aldosterone)
- Renal failure (renal artery stenosis)
- AKD
Who should we not give ACE inhibitors to?
- Patients w./ CKD
- Pregnancy
- Breastfeeding
What are some of the important drug interactions with ACEi to note?
- Drugs that increase K+
- NSAIDs
- Other antihypertensive agents
Give 2 examples of angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs).

- Candesartan
- Losartan

How do ARBs act to reduce BP?
(ARBs= Angiotensin-II blockers= AT1 Receptor blockers)
Angiotensin II acts on AT1 and AT2 receptors
Directly target AT1 receptors (more effective at inhibiting Angiotensin II mediated vasoconstriction - chymase production)

Why do ARBs not cause a dry cough or angioedema but ACE inhibitors do?

Angioedema is an area of swelling of the lower layer of skin and tissue just under the skin or mucous membranes
ARBs have no effect on bradykinin
Less effective in low- renin hypertensives
What are some of the contraindications of ARBs inhibitors? (3) Who should they not be given to? (3)
Contraindications
- Hyperkalaemia (low aldosterone)
- Renal failure (renal artery stenosis)
- AKD
Who should we not give ACE inhibitors to?
- Patients w./ CKD
- Pregnancy
- Breastfeeding
What are some of the important drug interactions with ARBs to note?
- Drugs that increase K+
- NSAIDs
- Other antihypertensive agents
How do CCBs (calcium channel blockers) work to reduce hypertension?
CCBs- target calcium initiated smooth muscle contraction
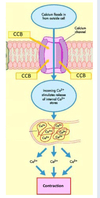
Different classes (3) interact with different sites on α1 subunit of VOCC
Outline the mechanism/site of action of the 3 classes of CCBs which are used to treat hypertension:
- State the names of drugs in each class
- State how they work
- Which class is the first line CCB in hypertension
- Which drug has selectvity for cerebral vasculature
- Which drug is use to treat arrythmia and angina

What are some of the side effects of dihydropyridines and who should it not be given to (contraindications)?
Side effects:
Ankle swelling
Flushing
Headaches
Palpitations
Contraindications:
Unstable angina
Severe aortic stenosis
What are the 2 important drug interactions to know for the dihydropyridine class of CCBs?

- Amlodipine + simvastatin - increase effect of statin
- Other antihypertensive agents
What are some of the side effects of phenylalkylamines and who should it not be given to (contraindications)?
Side effects:
- Constipation
- Bradycardia (iv)
- Heart block
- Cardiac failure
Contraindications:
- Poor left ventricular function
- AV nodal conduction delay








