5 - Limbic System Flashcards
(45 cards)
What is the function of the limbic system and where is it located?
Interconnected cortical and subcortical structures that link visceral states and emotion to cognition and behavior.
Limbic structures are interposed between the neocortex and the brainstem. (Limbis means border)
What is integrated within the limbic system?
Cortical information and hypothalamic impulses. The goal of this is homeostasis (autonomic regulation), olfaction, memory, and emotion (HOME).
What is the funciton of each area?
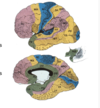
Limbic areas in green.
Higher-order (heteromodal) associated areas in pink.
Modality-specific (unimodal) association areas in yelllow.
Primary sensory and motor areas in blue.
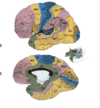
What is Papez’s circuit?
Cingulate
Hippocampus
Fornix
Anterior thalamus
Mammillary bodies
What contribution did MacLean make to the understanding of the limbic system?
Coined term limbic system and incorporated Papez’s ideas into a model that hasn’t changed much since.
Expaned it to include: parts of hypothalamus, septal area, orbitofrontal cortex, nucleus accumbens, and the amygdala.
What is considered the outer core of the limbbic system? What is the function of each region?
- Cingulate cortex: rostral - emotions; caudal - visual spatial and memory
- Orbital frontal lobe: personality, behavior control, self-awareness
- Temporal lobe (hippocampus, parahippocampus, entorhinal cortex): memory
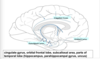
What are the inner core structures of the limbic system?
- Hypothalamus
- Amygdala
- Septum

What part of the limbic lobe is the hypothalamus in? What is it’s function?
Inner core
Pleasure center, autonomic, endocrine integration, neurons project to the pituitary, maternal behaviour, BP, feeding, temperature regulation, and immune response.
What part of the limbic system is the amygdala in? What is it’s function?
Inner core structure.
Preservation of self behaviors, emotion, social behavior, aggression and defense response, sexual behavior, affective significance of visual stimuli, affect of faces, and affective regulation.
What part of the limbic system is the septum in? What is it’s function?
Inner core structure.
Preservation of species behaviors, sexual behavior, emotionality.
What connects the hippocampus to the mammillary, the anterior thalamus, the septal nuclei, and the nucleus accumbans?
The fornix.

What connects the mammillary bodies and the hypothalamus to the anterior thalamus, hypothalamus, and the septum?
The mammillothalamic tract.
What connects the entorhinal cortex and the cingulate gyrus to the dentate, parahippocampal gyrus, hippocampus, the amygdala, and the midbrain?
The perforant path.
What is the function of the fornix?
It’s the main projection tract connecting the hippocampus and the mammillary boy.

What is the function of the mamillothalamic tract?
Originates from the mammillary bodies and terminates in the anterior and dorsal nuclei of the thalamus.

What is the major efferent path from the limbic system?
The fornix: connects the hippocampus with the septum and the mammillary bodies.
What is the major afferent path to the hippocampal formation?
Perforant path: connects the entorhinal cortex with the dentate gyrus

What is the funcion of the anterior thalamic projections?
Connect to the orbitofrontal and anterior cingulate cortex. (green)

What is the path of the cingulum fibers?
Run from the amygdala and parahippocampus to the frontal lobe/cingulate. (red)

What is the path of the uncinate fasciculus?
Connects the anterior part of the temporal lobe with the orbital and polar frontal cortex. (light blue)

What justified the concept of the limbic system being a true system?
- Common psychiologic and neurochamical properties
- Intricate anatomic and mostly reciprocal connections
- Common behavioral associations
What virus has specific affinity for the limbic regions? Shat are other common psycsiologic and neurochemical properties of the region?
Herpesvirus
Susceptible to kindling and development of suizure foci.
High density of cholinergic innervation and opiate receptors.
What effect can herpesvirus have on the brain?
Herpes encephalitis in the orbito-temporal-frontal regions.
Results in severe behavioral abnormalities and memory impairment.

What are the three overlapping functional sections of the limbic system?
Hippocampal and parahippocampal regions: memory and spatial orientation
Temporal-amygdala-orbitofrontal: integration of visceral sensation and emothion with semantic memory and behavior
Medial “default network”: autobiographical memory and introspection/self-directed thinking





