63 Clinical: Stroke Flashcards
(44 cards)
1
Q
Stroke
- How often is this a cause of death in the US?
A

2
Q
Stroke
- What is TIA?
- What is the difference between embolic and thrombotic stroke?
- Differentiate between ischemic, hemorrhagic and hypoxic stroke/
A
Stroke
- What is TIA?
- A Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA) is often called a mini-stroke, but it’s really a major warning. TIA is a temporary blockage of blood flow to the brain. Since it doesn’t cause permanent damage, it’s often ignored. But this is a big mistake. TIAs may signal a full-blown stroke ahead.
- What is the difference between embolic and thrombotic stroke?
- Differentiate between ischemic, hemorrhagic and hypoxic stroke/

3
Q
Ischemic Stroke
- What amino acid is released upon material occlusion?
- What does the above answer do to cells?
A

4
Q
Ischemic Stroke
- What are the common causes of this? (5)
- What are the uncommon causes of this? (6)
A

5
Q
Ischemic Stroke
- What are the 6 most common risk factors for this?
A

6
Q
Ischemic Stroke
- For thrombotic strokes from this category:
- How do these present?
- When do they occur?
- What is the major cause?
A

7
Q
Ischemic Stroke
- For embolic strokes from this category:
- How do these present?
- When do they occur?
- What is the major cause?
A

8
Q
Ischemic Stroke
- For lacunar strokes from this category:
- How do these present?
- When do they occur?
- What is the major cause?
A

9
Q
Hemorrhagic Stroke
- For intracerebral hemorrhages from this category:
- How do these present?
- When do they occur?
- What is the major cause?
A

10
Q
Hemorrhagic Stroke
- For subarachnoid hemorrhagic strokes from this category:
- How do these present?
- When do they occur?
- What is the major cause?
A

11
Q
Hypoxic Stroke
- For anoxia strokes from this category:
- How do these present?
- When do they occur?
- What is the major cause?
A

12
Q
A
13
Q
Diagnosis of Strokes
- What arteries are associated with anterior circulation? (3)
- What are the 4 most common signs/symptoms associated with this?
- What arteries are associated with posterior circulation? (8)
- What are the 2 most common signs/symptoms associated with this?
A

14
Q
Diagnosis of Strokes
- What artery supplies each colored area?

A

15
Q
Watershed infarcts
- What is a watershed Zone?
- What can cause these, and what arteries are implicated?
- Anterior Water Shed Infarcts
- What arteries are these between?
- What 3 signs/symptoms usually occur?
- Posterior Water Shed Infarcts
- What arteries are these between?
- What 2 signs/symptoms usually occur?
A

16
Q
Clinical Dx Of Stroke
- Clinical Finding
- Contralateral Leg Weakness
- What circulation is implicated?
- What artery is implicated?
- Contralateral Leg Weakness
A

17
Q
Clinical Dx Of Stroke
- Clinical Finding
- Contralateral face arm> leg weakness with sensory loss, visual field loss, apraxia/aphasia
- What circulation is implicated?
- What artery is implicated?
- How would the above answer change if the patient had neglect instead of apraxia/aphasia?
- What is important to know about these findings?
- Contralateral face arm> leg weakness with sensory loss, visual field loss, apraxia/aphasia
A

18
Q
Clinical Dx Of Stroke
- Clinical Finding
- Contralateral motor or sensory deficits WITHOUT cortical signs?
- What circulation is implicated?
- What artery is implicated?
- What else is important to know about this presentation?
- Contralateral motor or sensory deficits WITHOUT cortical signs?
A

19
Q
Clinical Dx Of Stroke
- Clinical Finding
- Contralateral Visual Field Loss
- What circulation is implicated?
- What artery is implicated?
- What else is important to know about this stroke?
- Contralateral Visual Field Loss
A

20
Q
Clinical Dx Of Stroke
- Clinical Finding
- Dysphagia, Dysarthria, tongue/palate deviation, and/or ataxia with crossed sensory-motor deficits (ipsilateral face with contralateral body?
- What circulation is implicated?
- What artery is implicated?
- What else is important to know about this stroke?
- Dysphagia, Dysarthria, tongue/palate deviation, and/or ataxia with crossed sensory-motor deficits (ipsilateral face with contralateral body?
A

21
Q
Midbrain Strokes
- What syndrome is shown?

A
Weber
22
Q
Midbrain Strokes
- Weber Syndrome
- What 3 fibers are affected?
A

23
Q
Midbrain Strokes
- Weber Syndrome
- What deficits are seen when these fibers are damaged?

A

24
Q
Midbrain Strokes
- What syndrome is shown?
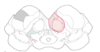
A
Claude
25
Midbrain Strokes
* Claude Syndrome
* What 2 structures are affected?

26
Midbrain Strokes
* Claude Syndrome
* What deficits occur when these structures are damaged?


27
Midbrain Strokes
* What syndrome is shown?
* What is it a combination of?
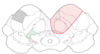
Benedikt
Benedikt = Claude + Weber
28
Pons Strokes
* What syndrome is shown to be more posterior?
* What syndrome is shown to be more lateral?
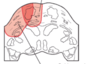
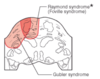
29
Pons Strokes
* What structures are affected by Raymond syndrome? (6)
* What structures are affected by Gubler syndrome? (2)


30
Pons Strokes
* What are deficits appear when the indicated structures are damaged?


31
Medulla Strokes
* What syndrome is shown to be more posterior?
* What syndrome is shown to be more lateral?


32
Medulla Strokes
* What structures are affected by Dejerine syndrome? (3)
* What structures are affected by Wallenberg syndrome? (4)
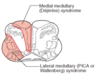

33
Medulla Strokes
* What are deficits appear when the indicated structures are damaged?


34
Acute Treatment and Work Up
* What 4 tests/labs do you need to do if you suspect a stroke?

35
Acute Tx for Stroke
* What is the main goal of treatment?
* What 3 things can accomplish this?
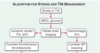
36
Algorithm for stroke and TIA
* If you suspect a stroke/TIA, what labs do you run before getting brain imaging?
* What is more common, Ischemic stroke/TIA OR Hemorrhages?
* What do you consider doing for Ischemic stroke/TIA?
* What do you consider doing for Hemorrhages?
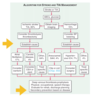
37
Algorithm for stroke and TIA
* Ischemic stroke/TIA
* What are the 3 main causes of this?
* Hemorrhages
* What are the 3 main causes of this?

38
Algorithm for Stroke and TIA
* What treatments are considered for all 6 of the causes?
* What do all potential treatments follow up with?

39
Treatment/Work Up
* Imaging
* What 3 types of imaging are conducted?
* Blood Work
* What 5 types of test are conducted?
* What 2 other tests can you conduct?

40
Stroke Prevention
* What 6 things can be done to decrease the risk for stroke?

41
Stroke Prevention
* What are the categories of the CHADS-VASc evaluation?
* What heart condition do the patients have?

42
Stroke Prevention
* When a patient has nonvalvular A-FIB, what is recommended when:
* The patient has a CHAD score of 0
* The patient has a CHAD score of 1
* The patient has a CHAD score of 2 or greater

43
Stroke Prevention
* Give the recommended TX for the following conditions:
* A-FIB
* Patent Foramen Ovale
* Patent Foramen Ovale + DVT/Hypercoag State
* Mechanical Heart Valve
* Infective Endocarditis

44
Stroke Prevention
* If a patient has carotid atherosclerosis, what 2 things can be done?



