Lecture 16: Adverse drug reactions Flashcards
What is an ADR?
Adverse Drug Reaction
“A response to a drug which is noxious and unintended, and which occus at doses normally used in man for prophylaxis, diagnosis, or therapy of disease, or for the modification of physiological features”
Basically just any unexpected, unintended, undesired or excessive response to a medicine.
medication errors?
mishaps that occur during prescribing, transcribing, dispensing, administering, adherence or monitoring of drugs. 25% of ADE caused by medication errors
Allergies and side effects?
Allergy: adverse drug reaction mediated by an immune response (eg. Rash, Hives)
Side effect: An expedcted and known effect of a drug that is not the intended therapeutic outcome (ie and ADR)
Adverse drug reaction classification
Mild -no change needed
moderate -change or additional treatment
severe -disabling, life-threatening, requires hospital admission
Type A
Type B
Type C
Augmented pharmacological effect (tricycling anti-d)
- extension of pharmacological effect
- often predictable and dose depedent (2/3 of ADR)
Bizarre (Malignant hyperpyrexia in anaesthesia)
- Idiosyncratic or immunological
- rare and unpredictable (dose independent)
Chronic effects (analgesic neuropathy)
- Associated with long-term use
- accumulation of dose/damage
Type D
Type E
Type F
Delayed effect (carcinogenicity or teratogenicity)
End of treatment (Stopping Corticosteroids - addisons)
Failure of treatment
-intended outcome of treatment not achieved
Drug allergy types?
Immediate -
Type 1 - anaphylactic, mediated by IgE and mast cells
Delayed -
Type 2 - cytotoxic, caused by IgE and IgM
Type 3 - immune complex, caused by IgE
Type 4 - cell-mediated, T-cell mediated
Classification of ADRs - DoTS
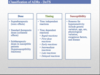
Why do ADRs matter?
3 most common causes?
- 4th leading cause of death in the US
- 6.5% of UK hospital admissions were found to be medication related
- 5% of people in hospital experience an ADR
- Hospital-acquired ADRs cost 380million pounds per year in UK
- Almost half of ADRs are preventable
- ADRs can cause death + serious harm, hospital admission or prolonged stay, and cost a lot
anticoagulants (intracranial bleeding)
opioids (constipation, sedation)
insulin (hypoglycaemia)
High risk patients?
- Young children and older adults
- multiple comorbidities (particularly renal and hepatic)
- Polypharmacy (No. of drugs)
- women
- race and genetic polymorphism
ADR prevention?
4 steps when you suspect an ADR?
docotr-based strategy
systems based strategy
educational programmes + accurate allergy lists
- Withdraw the trigger medicine
- Record the suspected ADR in the drug chart
- Inform the patient, care giver and family doctor
- Complete a CARM adverse drug reactions form


