Basic Science & Non-Tumor pathology Flashcards
Which bone graft substitue disappears the most quickly in vivo?
Calcium sulfate
What is the rate of decay in bone mass after skeletal maturity?
After menopause in women?
0.3-0.5% per year after skeletal maturity
a further 2-3% for untreated women during the decade after menopause
What kind of collagen is fibrocartilage?
Type 1
same as bone
So scar = type 1 collagen
What cell type accounts for 90% of the adult skeleton?
osteoCYTE
rhBMP-2 is approved for what uses?
Single level ALIF from L2-S1 in DDD with a fusion device
open tibial shaft fratures stabilized with an IM N and treated with 14 days of initial injury
What is the bending rigidity of a plate proportional to?
Thickness ^3
What is false about osteocalcin?
- It is the most abundant noncollagenous protein of bone
- It is secreted by osteoclasts
- It is involved in mediating calcium homeostasis
- It has been used as a biochemical marker of bone formation
- It is part of the organic matrix of bone
2
It is secreted by osteoBLASTS
What is the increase in mortality risk after a fragility fracture of:
vertebra
hip
Vertebral fragility fracture: 15% increase
Hip fragility fracture: 20% increase
How much devascularization does reaming cause?
It devascularizes 50-80% of the cortex
Muscle duration and speed of contraction are most dependent on what?
Fiber type
Type II (fast twitch) contract faster, stronger and fatigue quicker
What happens with removal of the AER?
Limb truncation
AER controls longitudinal growth

Name the rare, but deadly, complication of Paget’s
What is the prognosis?
Paget’s Sarcoma
secondary transformation into osteosarcoma > chondrosarcoma > spindle cell sarcoma
<1%
5 year survival <5%
Distraction osteogenesis - bone forms by what type of ossifciation?
intramembranous (primary) ossifciation
Name 4 results of joint immobilization on articular cartilage
cartilage thinning
tissue softening
reduced proteoglycan content
cartilage erosion
What’s the role of collagen in artiular cartilage?
Prevent swelling of articular cartilage that would otherwise occur due to the effect of aggrecan in drawing in water
What is the mechanism of botox?
Inhibition of ACh release from presynaptic vesicles
How do local anesthetics works?
Interfere with conduction (depolarization)
Rate of decrease of vertebral fragility fractures after bisphosphonate treatment at 1 & 3 years?
1 year: 60% decrease
3 years: 40% decrease
Also decreased non-vertebral fraglity fractures 40%
Area of growth plate pathology in rickets
zone of provisional calcification
This is why there is a widening of physis on xray, bc the physis doesn’t ossify!
3 radiographic findings in osteopetrosis
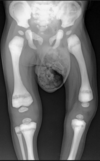
Rugger jersey spine
Erlenmeyer flask distal femur
Thickened cortex/lack of a IM canal
Phases of ligament healing
inflammatory
- neutrophils & macrophage mediated with growth factors involved
Proliferative
remodeling
maturation
What happens to water content of cartilage with normal aging? in OA?
Decreases with normal aging
Increases with OA
What supplies the inner and outer parts of bone? (blood vessels)
Nutrient artery system supplies inner 2/3
is a high pressure system
Periosteal system supplies outer 1/3
is a low pressure system
50 year old DM patient comes in with sudden onset of unilateral leg weakness, absent reflexes on that side and weight loss of about 15 - 20 lbs. No history of radiculopathy or back issues. Diagnosis? 1 differential
Diabetic lumbosacral plexopathy (basically diabetic neuropathy)
Acute, stepwise onset of unilateral weakness
Associated with poor diabetic control, absent reflexes and weight loss (up to 40 lbs)
dDx: tumour
When does enchondral ossification occur in fracture healing (what stage)?
repair
Why don’t you want your anesthesiologist to use nitrous oxide as an inducin agent for spine or pelvic surgery?
Causes abdominal distension and makes fluoroscopy difficult to interpret
Descirbe direct insertion of ligament or tendon onto bone:
= fibrocartilagenous insertion
via 4 transition zones:
Zone 1: tendon or ligament
Zone 2: fibrocartilage
Zone 3: mieralized fibrocartilage
Zone 4: bone
Effect of tapping prior to screw insertion on pullout strength
decreases it
The femur radiograph of a healthy 25-year-old female is compared to the femur radiograph of a healthy 85-year-old female:
What best describes the 25-year-old’s femur in terms of cortical thickness and medullary canal volume?
Increased cortical thickness
Decreased medullary canal volume
As you age, you get thinner cortices and therefore larger canal volumes
Function of PTH
Increases blood Ca
Decreases phosphate
What is the effect of physiological stress on cartilage?
physiologic stress stimulates chondrocyte synthesis and protects against chondrolysis
vs
excessive stress promotes chondrolysis (in-vitro only)
Why do you place a concave bend when putting on a compression plate for a transverse fracture?
To achieve compression on both the near and and far cortices
After 5 year, what percentage of donor and recipieint chondrocytes will be present on an osteoarticular allograft?
None
5 years after implantation, allograft articular cartilage is completely acellular
No donor or recipient chondrocytes will be present
What is the primary pathologic process in Paget’s disease?
Increased osteoclastic mediated bone resorption
excessive bleeding during THA, malalignment during TKA
High Cardiac output heart failuire
Normal Ca serum, elevate bone turnover markers
Paget’s sarcoma
- less than 1% will develop malignant Paget’s sarcoma (secondary sarcoma)
- osteosarcoma > fibrosarcoma and chondrosarcoma
- most common in pelvis, femur, and humerus
- poor prognosis
- 5-year survival for metastatic Paget’s sarcoma < 10%
- treatment includes chemotherapy and wide surgical resection
Where do SH I fracture occur through?
zone of provisional calficiation (part of hypertrophic)
Name the only irreversible COX inhibitor
ASA
What side of the fracture should compression plating be done?
Tension side
But may be sacrificed to have a plate lie flat on the bone
(JAAOS 2014)
Diagnosis and cause of x-ray findings (see pic)

Osteogenesis imperfecta
Multiple bands caused by bisphoshonate usage (specifically Pamidronate)
Function of Retinoic acid in embryology. What happens when it’s knockedout
Regulates zone of polarizing activity
if blocked, get limb bud abortion
WNT7 function
dorsoventral patterning of limb
A 27-year-old male undergoes intramedullary nailing of a midshaft tibia fracture with static locking proximally and distally. There is minimal healing noted 3 months postoperatively and the decision is made to dynamize the nail. For intramedullary nail dynamization, an interlocking screw should be placed in which of the holes shown in Figure A?

A
see pic

what is the effect of bisphosphonates take post lumbar fusion?
Decreases fusion rates
(it increases the fusion mass itself but decreases the actual rate of fusion)
When do you achieve peak bone mass?
Between at 16-25
Carrying a load in the ipsilateral hand does what to joint reactive forces at the hip?
decrease it
Increases A

Stages of tendon healing
Hemostasis
Inflammation
Organogenesis (type III Collagen)
Remodeling(type 1 collagen)

Main risk of interscalene block?
sensory neuropathy
Investigations for Gaucher’s
CBC - thrombocytopenia, anemia
cardiac exam: murmurs
GI exam: hepatosplenomegaly
AR deficiency of B-glucocerebrosidase, lysosomal disease, Askenazi Jew, Osteonecrosis (bone crisis), deformity of D. or P.femur.
Bone marrow histo shows binucleate cell filled with glucocerebroside,
What is the torsional rigidity of solid and cannulated IM nail proportional to?
Solid: r^4
Cannulated: r^3
Describe the screw home mechanism
The tibia (not femur) ERs 5 degrees during the last 15 degrees of knee extension
This locks the knee, decreasing work performed by the quad during standing
(so the femur IRs)
What is the only zone where articular cartilage progenitor cells have been found?
Superficial (tangential) zone
Inheritance of osteopetrosis?
AR: infantile form (fatal), intermediate form - carbonic anhydrase II dysfunction)
- Frequent fracture, blindness, deafness (enlarging skul), anemia (marrowc rowding), frequent infections (osteo of the Jaw)
AD: Adult form (MC, benign)
Avoid nails for femurs, Plate. Navigation for arthroplastyl, infection risk
Where do muscle strains and tears normally occur?
Myotendinous junction
Patient with degenerative arthritis and this urine sample.
Diagnosis?
What is the pathophys?

Ochronosis (Alkaptonuria)
Degenerative arthritis + black urine
Due to defect in homogenistic acid oxidase enzyme
Leads to excess deposition of homogenistic acid in joints
No treatment available
How do bisphosphonates work?
inhibits osteoclasts by inhibiting ruffled border (where the bone resorption occurs)
NITROGEN BISPHOSPHONATES -1000-fold more potent than non-N
- Block farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase - Results in a loss of GTPase formaton
- key to ruffled border formaton and cell survival - cell apoptosis
Non-NITROGEN BISPHOSPHONATES
- Metabolized into a nonfunctonal adenosine triphosphate (ATP) analogue
- induces apoptosis
4 factors that can alter neuromonitoring signals:
Halogenated anesthetics
Nitrous oxide
Hypothermia
Hypotension
What does the zone of polarizing activity do?
What 4 molecules control/are associated with it?
Controls AP development of the limb bud
THINK: ZPA controls PA (posterior to anterior) growth
Duplication mutation results in mirror-image duplication
Which phase of bone healing is abnormal in OI?
remodeling
So they heal normally, but don’t remodel so are more fragile
7 orthopaedic manifestations of osteogenesis imperfecta
Bone fragility and recurrent fractures
ligamentous laxity
short stature
scoliosis
codfish vertebrae
basilar invagination
olecranon apophyseal avulsion fracture
What happens to chondrocytes in articular cartilage with normal aging
Decreases in amount (hypoplastic)
increases in size (hypertrophic)
Why is the increased water content of cartilage in OA pathologic. Describe in 3 lines
Increased water content leads to:
increaed permeability of cartilage
decreased strength of cartilage
Decreased Young’s modulus of elasticity
Where does Vit D get hydroxylated?
Where does it exert it’s effect?
Hydroxylated in Liver (25-OH) & Kidney (1,25-OH)
Increases calcium absorption from intestines and bone, along with PTH
No effect for calcium in kidneys
Factor deficiencies for hemophilia A & B
A: FVIII
B: FIX
What common type of rickets has low phosphate, normal calcium and normal PTH?
X-linked hypophosphatemic

Genetics: what is imprinting?
Genetic phenomenon where certain genes are expressed in a parent-or-origin specific manner
ie:
Angelman
Prade-willi
What is false about osteocalcin?
A. It is the most prevalent non-collagenous protein in bone
B. It is expressed by mature osteoblasts
C. It is considered a marker for osteoblast differentiation
D. It is a glycoprotein that binds calcium
E. Higher levels are correlated with increases in bone mineral density during osteoporosis treatment
D
It is not a glycoprotein that binds calcium, however it is involved in calcium homeostasis
osteocalcin
- most abundant non-collagenous protein in the matrix (10%-20% of total)
- produced by mature osteoblasts
- function
- promotes mineralization and formation of bone
- directly involved in regulation of bone density
- attracts osteoclasts
- signaling
- stimulated by 1,25 dihydroxyvitamin D3
- inhibited by PTH
- clinical application
- marker of bone turnover
- can be measured in urine or serum
- marker of bone turnover
8 risk factors for fungal infection
JAAOS 2014

Function of HOX
segementation of limbs
radio-ulnar & tib/fib patterning of limbs
In hemophila, 2 options for synovectomy
Which is better?
Surgical synovectomy
Radioactive synoviorthesis: Destruction of synovial tissue with intra-articular injection of radioactive agent)
Radioactive synoviorthesis is better
Has been shown to reduce recurrent bleeding more than surgical synovetomy