Repro Flashcards
Three parts of the urethra?
Prostatic
Membranous
Penile

Difference between cat and dog prostate?
Cat prostate just goes around the dorsolateral aspect of the prostatic urethra Dog is all the way around
Where does the external urethral orifice lay in a female
vestibulovaginal junction
Retrograde urethragram is done with what type of contrast?
Iodinated, water soluble
What views are need to assess the urethra?
Laterals with extended and flexed hips
Lateral obliques
VD
How much contrast should be given for urethragram?
5-20ml (50/50 solution)
Take rads while giving the last 2 ml
Another way to do a urethragram in a female is?
vaginourethrocystogram
Foley in the vestibule
catheter in the vagina
Clamp vulva shut with foreceps
Fill vagina up with 1ml/kg of contrast and it will leak into the urethra
What are complications of urethrogram?
Iatrogenic rupture
Infection
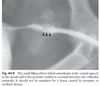
What is this?

Urethral plug/obstruction in a male cat
How can you tell the difference between a stone and air bubble on urethrogram?
Bubbles are smooth and stones are rough edges

The os penis is sometimes mistaken for a urethral calculi when it has a?
Separate center of ossification - rare

What is your ddx?

Thickening of the urethral
Neoplasia (TCC)
Inflammation (granulomatosis urethritis)
How do you differentiate a stricture from inadequate dilation or spasm?
Irregular margins
Dilations of urethra prox from the lesion
Urethral fistulas…are they a thing and if so, when do they happen.
Yes
Previous trauma
congenital
What are urethrograms good at diagnosing?
Strictures (congenital, inflammatory, neoplasia)
Calculi
DDx for enlarged prostate?
BPH
Prostitis
Cyst
Neoplasia (prostatic or Testicular)