Microbiology Flashcards
Outer surface (cell wall/ membrane) of viruses, bacteria, fungi and protozoa/ helminths
Viruses: Protein capsid made up of capsomeres
Bacteria: Cell wall made up of peptidoglycan
Fungi: Cell wall made up of chitin
Protozoa and helminths: flexible membrane

Helminths
Multicellular worms that infest body, mainly GI tract.
Transmission can be direct or indirect via an intermediate non-human host.

Protozoa
Single cell organisms. Have a dormant and active stage. Acquired by contaminated water.
Fungi
Single cell or brainched or both organisms. Have a cell wall made up of chitin. Disease caused by environment or part of the normal flora.

Bacterial cell wall structure
Multilayered structure mainly composed of peptidoglycans, which is glycan chain and tetrapeptide chain.
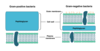
Difference between Gram + and Gram - cell wall
Gram +: thick cell wall, no outer membrane or lipopolysaccharides, no porins. Gram -: Thin cell wall, outer membrane containing lipopolysaccharides, as well as porins.

Structure of capsule in Bacteria
gelatinous layer outside cell wall made up of polysaccharides.
Determinant of virulence. Helps with adherence. Helps with identification of a bacteria in lab.

2 Roles of pilli
- Attachement
- Conjugation (sexual reproduction)
Spores in Bacteria
produced by some gram positive bacteria, highly resistant structures resistant to harsh conditions.
Components of viruses
DNA or RNA genome, capsid core, polymerase protein. Sometimes envelope.

name of the viral genome enclosed by capsid protein coat
and
Subunits of capsid
nucleocapsid
capsomeres
Icosahedral capsid
made up of 20 equilateral triangular faces arranged around the surface of a sphere. Each triangle is made of min 3 proteins.

Helical capsid
Proteins are arranged in a helix around the DNA.

Viral Envelope
Lipid bilayer from host cell membrane surrounding certain viruses.
Has glycoproteins attached to its surface (spikes). It determines the stability of virus: enveloped ones cannot live outside host.

Importance of viral surface protein
Attach to membrane proteins and binding sites for antibodies.










