Fatty acid metabolism Flashcards
Lipid is a broad term and what does it encompass?
Fats, oils, waxes and other hydrophobic molecules such as cholesterol
What are fatty foods rich in?
Triglycerides (TG)
What makes something a fat or an oil?
Fats= solid at RT oils= liquid at RT
Both are triglycerides
Whats another name for a triglyceride?
Triacylglycerols (TAG)
Whats the structure of triglycerides?
Three fatty acids that are ester linked to glycerol backbone

What makes something a fatty acid?
- long chain (12-24 C) hydrocarbons (acyls- long hydrocarbon chains)
- Methyl groups –>–>–> COOH group
- 0 or more double bonds

What are the structure that can be made when a double bond is present?
How does this change a molecule?
- Cis or trans can change properties and therefore change what molecule it is
- Fatty acids can become more curled depending on how many double bonds are present (poly-cis)

What are the different ways that fatty acids can be named?
Give an example for each using Oleic acid
- Common name: Oleic acid (oleate)
- Systematic name: cis-∆9 octadecenoic acid
- Omega or n system name: C18:1 (n-9)
What can be a problem with systematic naming ?
They can start from different ends which may change the number carbon being referred to. E.g. systematic from COO- group whilst omega from CH3 group

How does the omega series naming work?
use this example

- Lowest number defines series. So, if first double bond at position 3 and other beyond, it would be omega 3.
- C18:2 (n-6) means 18 carbon chain, has 2 double bonds, lowest one at position 6
Humans have the ability to alter their fatty acids, what enzymes help with this and what is their role?
Elongases- increase chain length by 2 carbons
Desaturases- add double bonds

When something is described as an essential Fatty acid (EFA) what does this mean?
Essential in biochemistry means that it is essential in the diet. But we as humans can’t make it so we have to eat it
give examples of essential fatty acids
- Humans don’t have the right desaturase to add double bonds lower than omega 9
- Omega 3 or omega 6 FA therefore have to come from the diet and are termed essential
Why would we need to alter fatty acids?
1. No need to for energy storage purposes
2. Membrane phospholipids
- Fatty acid length –> bilayer thickness
- Degree of unsaturation –> membrane fluidity
- Tissue-specific membrane composition e.g. brain is roughly 60% fat, enriched in omega 3 and 6
- Some FA are precursors to signalling molecules (e.g. prostaglandins, leukotrienes, thromboxane’s)
How are fatty acids obtained from the diet?

How are lipids in food digested?
- Majority of lipid in food is triglycerides
- Digested by pancreatic lipases
- Can now cross membrane into intestinal cells

Tell me about the absorption/ assimilation of triglycerides?

Tell me about the structure of a Lipoprotein?
What do they transport?
Give an examples of types of lipoproteins?
- A mixture of lipid and protein
- Phospholipid and cholesterol outer layer
- Triglyceride and cholesterol ester inner core
- Transport from gut to adipose tissues uses chylomicrons (up to 1 um in diameter)
- ApoB48, ApoC2 (important as binds to capillaries), ApoE

How are fatty acids taken up into adipose tissue?
- Endothelial cells have lipoprotein lipase attached on the luminal side
- Lipoprotein lipase cleaves off fatty acids when enter cells
- When chylomicron has offloaded most of the TG it is called a remnant and is removed from circulation by the liver
Tell me the stages to TG synthesis in adipose tissue of the liver (lipogenesis)
Name the enzymes and give the structures involved
This is different to intestinal synthesis

Give a summary of fatty acid metabolism?

What is the energy contained within a fatty acid?
- *Glucose** –> 17 KJ/g (4 kcal/g)
- *Fatty acid (palmitic)** –> 38 KJ/g (9 kcal/g)
Whats an advantage of fatty acids?
They form dense energy stores
Why are fatty acids used as opposed to glucose?
Glucose –> glycogen + 2x mass of water (H bond with water)- not efficient to store as a majority is water
Fatty acids –> triglycerides + no water (better as are hydrophobic so don’t store water, so all mass is energy molecules)
Tell me about Triglyceride hydrolysis for adipose tissue?
Tell me the enzymes used and their function
- Shrink and grow as TG are absorbed
- Every fatty droplet is surrounded by a shell of protein which restricts access to TG
- Only break down TG under certain conditions
- Phosphorylase perilipin coat
- FA chains removed one at a time
- 3 enzymes are above, have different substrates but same function

What does free fatty acid bind to?
Human serum albumin (HSA)
What is TG broken down into and by what?
TG is broken down into 3x FA and by HSA
What are fatty acids picked up by and why?
Picked up by major carrier proteins HSA
As too hydrophobic to be transported in blood on its own (can pick up 3x FA and transport to rest of body)
Tell me about fatty acid entry into cells?
FA are released from HSA and travel to the outer membrane of a mitochondrion where they are activated
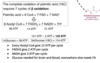
What are the two steps to fatty acid activation?
FA + CoA –> Acyl-CoA
- ATP- consuming process catalysed by Acyl CoA synthetase
- conversion of AMP to ADP requires another ATP (-2 ATP overall before in mitochondria)

Tell me about Acyl-CoA entry into the mitochondria
- Acyl- CoA can cross outer mitochondrial membrane
- CoA must be swapped for carnitine to cross the inner mitochondrial membrane via a carnitine acyltransferase enzyme
- Acyl- carnitine is transported across the bilayer by a translocase antiporter
- Acyl chain is reattached to CoA once in the matrix

When a fatty acid is converted to acetyl CoA and enters the TCA cycle, what are the products of this reaction?
8 hydrogens
2 Carbon dioxides

In beta oxidation, what are Fatty acids (e.g. C16:0) catabolised into?
2C units
In beta oxidation, what bond is cleaved?
the beta carbon