Cell adaptation Flashcards
What are the different cellular adaptation?
Cellular adaptations are reversible and 4 cellular adaptations are
- Hypertrophy- increase in size
- Hyperplasia- Increase in number
- Atrophy- decrease in size
- Metaplasia- One adult cell replaced by another adult form of cell.
What type of cells undergo hypertrophy and give few examples of physiological and pathological hypertrophy.
Permanent cells undergo hypertrophy. eg: Skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle. 1. Physiological eg- Sk muscle (body builders), uterus (Hypertrophy and hyperplasia) 2. Pathological- eg Urinary bladder (BPH), LVH (HTN, myocardial infarction, valvular abnormalities)
Mechanism of Hypertrophy (with referance to cardiac muscle)
Three steps
1) Actions of mechanical sensors
- these come into play following increased workload
- Growth Factors: TGF-B, insulin like growth factor 1 (IGF1), fibroblast growth factor
- vasoactive agents: a-adrenergic agents, endothelin-1, angiotensin II
2) Signal transduction pathways
- PI3K/AKT pathway: involved with physiologic type
- G-protein-coupled receptor pathway: important for cardiac hypertrophy
3) Transcription pathways
- GATA4, nuclear factor of activated T-cells (NFAT), myocyte enhancer factor 2 (MEF2)
- increase the synthesis of contractile protein

Assiociated changes in pathological cardiac muscle hypertrophy?
1) switch of contractile proteins from adult to fetal or neonatal forms
- α isoform of myosin heavy chain is replaced by β isoform
β isoform:
- slower, more energetically economical contraction
2) atrial natriuretic factor (ANF) - gene expression for ANF in both atrium and ventricles in embryonic heart
Types of cardiac muscle hypertrophy? and give few conditions for each.
what type of heart failure will be seen in these hypertrophy?
2 types-
- Concentric- sarcomeres arranged parallely
Eg: Pressure overload conditions. Aortic stenosis, coarctation of aorta, sytemic hypertention, Hypertrohic obstructive cardiomyopathy (HOCM- genetic condition)
Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF). S4 heart sound heard (compliance of the ventricular muscle is decreased)
- Eccentric- sarcomeres arranged in series.
Eg: Volume overload conditions. Aortic regurgitation, Mitral regurgitation, Anemia, dilated cardiomyopathies.
Heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF). S3 Heart sound heard( volume overload)
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM)- Cause, Gross and microscopic features?
Most common cause of sudden death in young people (familial).
- autosomal dominant disease of the heart muscle
- affected genes include β-myosin heavy chain (most common), myosin-binding protein C, cardiac troponin T and I, α-tropomyosin, actin, titin, and myosin light chains
- Gross- asymmetric septal hypertrophy with a small left ventricular cavity
- Micro- -myocardial disarray consists of short runs of severely hypertrophied fibers
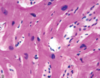
What is hyperplasia?
Mechanism of hyperplasia.
Give some examples of physiological & Pathological hyperplasia.
Increase in number of cells.
Mechanism- increased formation of local growth factors and hormones
- Physiological – Breast (puberty & pregnancy)
- Pathological-
- Endometrial hyperplasia- PCOD- glandular proliferation (risk carcinoma)
- BPH- normal aging process- DHT- both glandular and stomal hyperplasia
- Parathyroid hyperplasia- ch renal failure
- Graves disease
- Islet of Langerhans hyperplasia – gestational DM
Endometrial hyperplasia- causes and microscopy.
Cause- Due to the action of unopposed estrogen on endometrium.
-inactivation of the PTEN tumor suppressor gene is a common genetic alteration in both endometrial hyperplasias and endometrial carcinomas
Eg:
- Post-menopausal women treated with hormone replacement therapy (HRT)
- This is associated with anovulatory cycles (PCOD)
Microscopy- increased proliferation of the endometrial glands relative to the stroma, resulting in an increased gland-to-stroma ratio
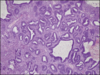
Benign prostatic hyperplasia - cause & Microscopy.
Cause- -prostatic levels of dihydrotestosterone (DHT) remain high with aging, even though peripheral levels of testosterone decrease due to high 5-alpha reductase activity.
Microscopy-
Most commonly affects the inner peri-urethral zone of the prostate. -variable proportions of stroma and glands hyperplasia.-hyperplastic glands are lined by two cell layers, an inner columnar layer and an outer layer composed of flattened basal cells.

Identify ?
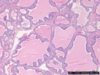
Graves disease-
Autoimmune condition.
- is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism
- incidence peaks between 30 and 50 years of age, more in females
- activating autoantibodies of the IgG1 subclass that are directed against the thyrotropin receptor are both specific for and central to Graves’ disease
- these antibodies stimulate thyroid hormone production that is uncontrolled by the hypothalamic–pituitary axis. Activating antibodies mimic the actions of thyrotropin at its receptor through the initiation of similar, but not identical, signaling
Microscopy-
Papillary projection & columnar epithelial lining with scaloping edges.

