9 - DM MedChem + Pharmacology Flashcards
(36 cards)
Wut dis is

Meglitinides
insulin SECRETAGOGUES
- *Repaglinide / Nateglinide**
- less hypoGlycemia than sulfonylureas*
wut dis is

DPP-4 INHIBITORS
LASS
Linagliptin - Tradjenta
Alogliptin - Nesina
Sitagliptin - Januvia
Saxagliptin - Onglyza
Additives for
Short Acting Insulin
“humulin R / novolin R”
- *Soluble Crystalline ZINC insulin**
- nothing else*
Effect in <30 minutes
PEAK = 2-3 hours
Lasts = 5-8 Hours
SGLT-2 Inhibitors
MoA / AE
C-D-E-E- gliflozin
invokana = canagliflozin
Inhibit the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) in kidney
Blocking the reabsorption of glucose
allowing for the glucose to pass into the URINE
SGLT2 = main site of glucose reabsorption in the kidney
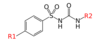
Sulfonylurea
SIDE EFFECTS + Drug Interactions
Glipizide + Glimepiride + Glyburide
hypoGlycemia
from too much GLUT4 taking in too much glucose
Metabolized by Liver -> excreted in kidney
Serum protein binding is HIGH
so it interacts with other HIGHLY PROTEIN BOUND DRUGS
Wut dis is?
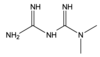
BIGUANIDE
Metformin
BI = two of the same thang, litta N’s
Alpha Glucosidase Inhibitor
MoA
- Hydrolyses Oligosaccharides -> smaller Monosacharides
- which are absorbed in the GI TRACT
-
Delay Digestion of Ingested Carbs
- Reducing POSTPRANDIAL Blood Glucose conc.
-
Glucose levels then rise more SLOWLY
- LESS insulin response is required
-
Do not stimulate Insulin release
- so they do not result in hypoglycemia
wut dis is
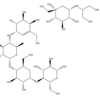
Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitors
ACARBOSE
Miglitol / Voglibose
Look like glucose ay ay
Meglitinides
MoA + SAR
Repaglinide + Nateglinide
Pancreatic Insulin Release = INSULIN SECRETAGOGUE
similar to Sulfonylureas
2 binding sites same as Sulfonylurea
+
1 Unique binding site
How is Insulin
Chemically Degradated?
NEUTRAL pH –> Deamination@ ASNB3
Acidic Conditions–>Deamination (rxn with water)
Oxidation of S-S Bridges –> aggregation / protein structure loss
INSULINASE = cleaves disulfide linkages in BLOOD
Rapid Acting Insulin Products
LISPRO
ASPART
GLULISINE
(LAG)
GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
MoA + Function
Liraglutide = Victoza / Dulaglutide = Trulicity
Exanatide / albiglutide
Incretin-Based Therapy
secreted in response to a meal, mostly by endocrine L-cells in small intestine
Stimulates first phase release of insulin from pancreatic beta cells
FA’s promote albumin binding & limits the DPP4 degradation
Glucagon Secretion / Gastric Emptying / Appetite
Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitors
AE + Drug Interactions
Acarbose + Miglitol + Voglibase
Carbs are SITTING IN THE GUT –> GI Issues
Flatuelence + Diarrhea + Abdominal Pain
from appearance of undigested cabs in the colon
What FACTORS affect the
Onset / degree / duration of action
of Insulin?
Primary Protein Structure
ANY change in the AA residues @ N/C-terminus of B-chain
Insulin CRYSTAL type
soluble/amorphous / crystal / microcrystal
ZINC OR PROTAMINE
Site of Injection
abdomen / upper arm / thigh / buttock
Smoker / Temp / Exercise Etc.
DPP4 Inhibitors
MoA + SAR
L-A-S-S -gliptin
_*slows the inhibition* of GLP-1_
MORE INCRETIN FUNCTION
reduce / slow down
Glucagon Secretion / Gastric Emptying / Appetite
Insulin Analog Creation
What do we make ADJUSTMENTS TO?
- We make adjustments to the C-Terminus of the B-Chain
- do not change Biological activity or immunogenicity
- Influence the rate of dimer formation & or Seperation
- All produced by RECOMBINANT DNA methods
wut dis is

SGLT2 INHIBITOR
Sodium-Glucose Cotransport Inhibitors
C-D-E-E - GLIFLOZIN
CANA / DAPA / EMPA / ERTU
Invokana / Farxiga / Jardiance / Steglatro
looks like the Alpha Glucosidase inhibitor but with MORE
TZDs
Side Effects + DI’s
Pioglitazone + Rosiglitazone
- *HEPATIC TOXICITY**
- similar to APAP*
Extensive P450 metabolism –>
metabolites excreted in URINE
PIOGLITAZONE decreases the
level of ESTROGEN oral contraceptives
Long-Acting Insulin Products
Detemir
Glargine
Degludec
(DDG)
wut dis is

TZDs
Rosiglitazone
Pioglitazone
TZD = THI-AZOLE
azole = Nitrogen 5 group + thi = sulfur too
Meglitinides
Side Effects / DI’s
Repaglinide + Nateglinide
LESS hypoGlycemia than sulfonylureas
Short acting / immediately taken before meals
metabolized by CYP3A4
Nateglinide is CYP3A4 + CYP2C9, less drug interactions
General changes on
Rapid Acting Insulin Analogs
L-A-G
c-terminus of B chain
Steric Hinderance / Charge-Repulsion
Reduced Self-Association
Absorbed MORE Rapily than regular insulin
General Changes on
Long-Acting Insulin Analogues
(Basal insulin)
GG-DD, c-terminus of B chain
Increased Self-Aggregation in SC tissue
Reversible Albumin Binding
Crystalline depot –> low levels of circuling insulin
ULTRALENTE
Zinc Insulin forming LARGE particles
delayed onset + prolonged duration of action
Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitors
MoA + SAR
Acarbose + Miglitol + Voglibase
Alpha glucosidase normally hydrolyses oligosaccharides –> monosaccharides which get absorbed from the GI tract
- DELAY* Digestion of CARBOHYDRATES
- REDUCING* PostPandial Blood Glucose (PPG)
SPREADS OUT the release of Glucose –> less insulin response required
DO NOT stimulate insulin release, no hypoglycemia