Abdomen Flashcards
(126 cards)
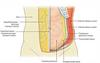
What are the laters of the abdomen lateral to rectus sheath?
Skin
Camper fascia (fatty layer)
Scarper Fascia (membranous layer)
Thin layer of deep fascia
External obliue muscle
Internal obliue muscle
Transversus abdominus
Fascia Transversalis
Extraperitoneal tissue
Parietal peritoneum

What are the abdominal wall layers anterior to the rectus sheath above arcuate line?
Skin
Campers fascia
Scarpas fascia
Thin later deep fascia
Anterior wall of rectus sheath
Rectus abdominus muscle
Posterior wall rectus sheath
Fascia transversalis
Extraperitoneal connective tissue
Parietal peritoneum

Abdominal wall layers in midline
Skin
Scarpers fascia
Campers fascia
Thin layer deep fascia
Linea alba
Transversalis fascia
Extraperitoneal connective tissue
Parietal peritoneum

Why is the membranous layer of superficial fascia important in the extravasation of urine?
Important as closed space that does not open into the thigh
Membranous rupture of the urethra may be followed by extravasation of urine into scrotum, perineum, penis and lower part of ant. abdominal wall deep to membranous layer of fascia
Urine excluded from thigh due to attachment of fascia to fascia lata
External oblique
origin: ribs 5-12
insertion: iliac crest and pubic tubercle
innervation: thoracoabdominal nerves

Internal oblique
origin: inguinal ligament, iliac crest, lumbodorsal fascia
insertion: ribs 10-12
innervation: thoracoabdominal nerve

Transversus abdominis
origin: inguinal ligament, costal cartilage, iliac crest and thoracolumbar fascia
insertion: conjoint tendon, xiphoid process, linea alba and pubic crest
innervation: thoracoabdominal muscles, subcostal

Rectus abdominis
origin: Crest of pubis
insertion: xiphoid process and sternum and costal cartilage 5-7
innervation: thoracoabdominal nerves

Pyramidalis
origin: pubic crest, pubic symphysis
insertion: linea alba
innervation: subcostal nerves

Rectus sheath
Formed by the aponeurosis of three flat muscles
Anterior wall - aponeurosis of external oblique and internal oblique
posterior wall - aponeurosis of internal oblique and transversus abdominis
ARCUATE LINE - midway from umbilicus to pubic symphysis where the posterior wall also lies anterior to the rectus sheath

What occurs at the arcuate line?
Inferior epigastric vessels pierce rectus abdominus and pass upward to anastamose with the superior epigastric vessels
\Post and ant rectus sheath passes anterior to rectus abdominus muscle below Arcuate line
Posterior abdominal wall
Quadratus lumborum
Psoas major
psoas minor

Quadratus lumborum
origin: iliac crest and iliolumbar ligament
insertion: transverse process of L1-L4
innervation: T12- L4

Psoas major
origin: T12-L5
insertion: Lesser trochanter
innervation: L1-L3

Psoas minor
origin: T12, L1
insertion: superior ramus of pubis
innervation: L1 action: flexion fo vertebral column

Fascia of the posterior wall
Psoas fascia - encloses psoas major & minor thoracolumbar fascia - divided into 3 layers, anterior, middle and posterior layer

Peritoneum
Continous layer divided into parietal and visceral peritoneum
Squamous epithelial cells from mesothelium
Parietal peritoneum
Somatic sensation thus well localised sensitive pain, laceration, temperature
Visceral peritoneum
Splanchnic mesoderm origin poorly localises, referred to pain in dermatomes
Sensitive to chemical and stretch
Retroperitoneal organ
SAD PUCKOR. Can be primary or secondary. Primary if developed and remain outside of parietal peritoneum.
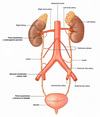
Suprarenal glands
Aorta
Duodenum (except 1st part)
Pancreas (except the tail)
Ureters
Colon (ascending & descending)
Kidneys
Oesophagus
Rectum
Peritoneal reflections
Mesentery
Greater omentum
Lesser omentum

Mesentery
Double layer of the visceral peritoneum
Connects the organs to the posterior abdominal wall
Small bowel
Transverse colon
Sigmoid mesocolon
Mesoappendix

Greater omentum
Greater curvature of stomach and proximal part of duodenum to anterior surface of transverse colon
Act as immunological barrier

Lesser omentum
Lesser curvature of stomach & proximal part of duodenum to liver
Hepatogastric ligament & hepatoduodenal ligament