Abdomen Flashcards
(77 cards)
Organs of midgut (in relation to blood supply)
Jejunum, ileum, cecum, ascending and 2/3 transverse colon
5 layers of facia of anterior abdominal wall
- superficial layer (fatty and membranous portions)
- deep (investing) layers: envelop muscle layers
- transversalis fascia
- extraperitoneal fascia
- peritoneum
contents of inguinal canal
Spermatic cord (ductus deferens, testicular artery, symphathetic nerve fibers)
round ligament of uterus
renal papilla
apex/tip of pyramid that points towards hilum
Where are external oblique muscles?

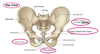
Where is the iliac crest?


what is the rectus sheath?
fascia surrounding the rectus abdominus muscle
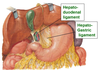
ligaments of the liver (2)
falciform ligament (round ligament)
coronary ligament
liver location
deep to ribs 7-11 on RHS, but crosses midline
cortex vs medulla of kidney
medulle in middle
cortex is outside
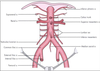
where does IVC begin?
begins anterior to L5 vertebra by union of common iliac veins (inferior to bifurcation of aorta), ascends to right of aorta
parietal vs visceral peritoneum
- parietal: lining internal surface of abdominopelvic wall
- visceral: investing the viscera such as the stomach and intestines
location of gall bladder
lies in gallbladder fossa on the visceral surface of the liver
Branches of superior mesenteric artery
- inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery
- jejunal and ileal arteries
- middle colic artery
- right colic artery
- ileocolic artery

Where is the pubic symphysis?


Where does the esophagus end?
terminates by entering the stomach at the cardial oriface to the left of the midline at the level of the 7th left costal cartilage and T11 vertebra
retroperitoneal organs (definitin only)
those that do not possess a mesentery. They lie within extraperitoneal layer of abdominal wall
Organs of foregut (in relation to blood supply)
esophahus, stomach, duodenum, liver, gall bladder, pancreas, spleen
action of internal oblique muscles
- compress, support abdominal viscera
- flex and rotate trunk to SAME side
attachements of internal oblique muscles?
- ribs 10-12, linea alba
- thoracolumbar fascia, iliac crest, inguinal ligament
branches of inferior mesenteric artery
- left colic artery
- sigmoid arteries
- superior rectal artery
mesentary
double layer of peritoneum that suspends some abdominal organs
rectus abdominus action
compress, support abdominal viscera
flex trunk
3 flat muscles of abdominal wall
external oblique, internal oblique, transverse abdominis