Abdominal Viscera and Collateral Circulation Flashcards
(68 cards)
The two curvatures of the stomach and their derivation:
- lesser curvature (ventral side of foregut before rotation)
- greater curvature (dorsal side of foregut before rotation)
Lesser omentum attachment and derivation:
- attachment: lesser curvature of stomach
- derivation: ventral mesentery of stomach
The two parts of the lesser omentum:
- hepatoduodenal ligament
- hepatogastric ligament
Derivatives of the stomach dorsal mesentery:
- gastrosplenic ligament
- greater omentum
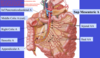
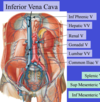
Label all:


Label:
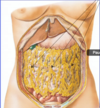
greater omentum
(arises from dorsal mesentery)
What structure is attached/fused to the posterior side of the greater omentum?
transverse colon
Label A and B:

- A = transverse mesocolon
- B = greater omentum
Greater Peritoneal Sac:
- All of the peritoneal cavity except for the lesser sac (omental bursa).
The greater peritoneal sac is subdivided into what two compartments?
- supracolic compartment
- above transverse colon and greater omentum (fused).
- infracolic compartment
- below transverse colon and greater omentum (fused).
The boundary between the supracolic compartment and infracolic compartment is:
- transverse mesocolon and greater omentum (which are fused together).

The three compartments of the peritoneal cavity:
- lesser sac
- supracolic (part of greater sac)
- infracolic (part of great sac)
What part of the greater omentum stretches from the greater curvature of the stomach to the level of the transverse colon?
gastrocolic ligament

Gastrocolic ligament:
- the part of the greater omentum above the transverse colon.
- a surgical entry into the lesser sac.
Label:


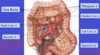
Contents of Supracolic compartment:
stomach, liver and spleen
Contents of Infracolic compartment:
small intestine, ascending colon, descending colon
The lesser sac communicates with greater sac via:
epiploic foramen
(foramen of Winslow)
The foregut gives rise to what organs?
PEG LSD
- Pancreas
- Esophagus
- Gallbladder
- Liver
- Stomach
- Duodenum (1, 2P parts)
The midgut gives rise to what organs?
JAILED CAT
- Jejunum
- Appendix
- ILEum
- Duodenum (2D, 3, 4, parts)
- Cecum
- Ascending colon
- Transverse colon (proximal 2/3)
The hindgut gives rise to what organs?
DESCENDING RATS
- DESCENDING colon
- Rectum
- Anal canal (upper part)
- Transverse colon (distal 1/3)
- Sigmoid colon
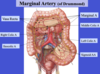
Celiac trunk is the blood supply to:
foregut and spleen
PEG LSD + spleen
Superior mesenteric artery is the blood supply to:
midgut + head of pancreas
JAILED CAT + head of pancreas
Inferior mesenteric artery is the blood supply to:
hindgut
DESCENDING RTS