Actual images Flashcards
(63 cards)
What does this picture of esophagus show?

kissing ulcers = sign that pill caused esophagitis
What is this finding on endoscopy?

candida esophagitis
What bug is causing this finding in the esophagus?

CMV esophagitis
What bug is causing this finding in the esophagus?

THis is herpest esophagitis
- Cell-cell detachment
- Multinucleation
- “Ground glass” nuclei
What do these findings on endoscopy suggest?

shows transverse rings = trachealization
possible sign of eosinophilic esophagitis
What is this lesion finding in the esophagus?

barrett’s esophagus = have intestinal like columnar epithelium with goblet cells
What normal part of the body is this?
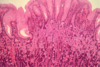
this is stomach = shows gastric fundic glands
What gastric cell type is this?

parietal cells
What disease of the stomach is this?

acute erosive gastritis
What is this finding in the stomach?

chemical gastropathy
see corkscrew gastric pits, dilated capillaries, loss of epithelial mucin
What kind of chronic gastritis is this?

This is autoimmune gastritis
- have intestinal and antral metaplasia
- chronic inflammation
- reduced glands
- loss of parietal cells
What type of malignancy is characterized by these cells?

these are signet ring cells
suggest diffuse adenocarcinoma
What type of gastric malignancy is this?

intestinal type gastric carcinoma
have gland formation
What disease of malabsorption is this?

abetalipoproteinemia = b/c theres fat filling the cells
What is this image show in the liver

this is alpha 1 antitrypsin deficiency
tiny pink dots are a1a that is abnormally folded and retained in the hepatocyte
What is this finding in the liver?

hepatocellular carcinoma
What is this finding in the liver?

hepatocellular carcinoma producing bile
What is this finding in the liver?

angiosarcoma = you can see the RBCs
What does this picture of the small intestine show?

cobblestoning of the intestinal wall = sign of Crohns
What does this finding in the intestine suggest?

Noncaseating granuloma –> suggests crohns
What is this disease?

ulcerative colitis = can easily see the line where it starts/stops
What type of IBD could this be?

ulcerative colitis = don’t see intramural inflammation like you would in crohns
What type of intestinal disease is this?

This is IBD = see crypt atrophy
What is this finding in the intestine?

This is cryptitis = see inflammation of the crypts with neutrophils; suggests IBD









































