Adaptations at Birth Flashcards
(7 cards)
1
Q
What happens to the lungs at birth?
A
Type II pneumocytes draw in fluid. This is why C-sections can cause problems
2
Q
How does the baby keep warm at birth?
A
Fatty deposits and Vermis
3
Q
What happens in relation to metabolism at birth?
A
Glucagon levels are increased to turn glycogen to glucose.
There is an increase in adrenalin
4
Q
What happens to the heart?
A
- Ductus arteriosus (P.A to aorta) closes to become the ligamentum arteriosum.
- Foramen ovalis (Between atrium) becomes fossa ovalis
- Ductus venosus closes (previously took blood from IVC to brain)
5
Q
What is a patent ductus arteriosis?
A
When the link between the PA and the aorta doesnt close at birth
6
Q
What are the symptoms of a patent ductus arteriosis?
A
- Murmur - Turbulent blood
- Breathlessness - More blood to lungs so cant get in oxygen
- Hepatomegaly - More to the PA so RA and RV so there is a back lof which blocks the liver
- Cardiomegaly/tachycardia - Heart is pumping more to get blood out so gets bigger and pumps faster
- Pale - Incrase in adrenaline to low oxygen
- Patent femoral pulse - as lower diastolic due to less in aorta
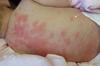
7
Q
What are some normal variants at birth?
A
- Tachypnoea
- tachycardia
- blue peripherally
- jaundice
- murmur
- anaemia - high RBC and parental o2 causes low EPO and anaemia after 4-6 weeks
- High clotting times so give vit k
- Erythema toxicum neonatorum