Alimentary Flashcards
(135 cards)
What are the predominant alimentary diseases for:
Small animals:
Ruminants and pigs:
Horses:
Small animals: alimentary neoplasia
Ruminants and pigs: infectious diseases
Horses: intestinal displacements/colic
What is the most common portal of entry of pathogenic agents into the alimentary system?
Ingestion
Cause of death of a calf was determined to be aspiration pneumonia due to incomplete fusion of the palatine shelves. What is a likely cause of this abnormality?

Ingestion of teratogenic plants by the mother during gestation (Veratrum californicum, lupines, poison hemlock)
*Palatoschisis can be caused by exposure to Griseofulvin in queens and mares, and steroids in primates
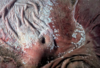
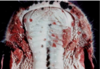
What disorder seen in this sheep can result in difficulty with prehension and mastication of feed?

Brachygnathia
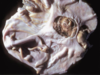
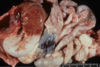
What disorder is seen in this horse?

Prognathia
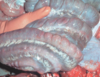
Step mouth is characterized by abnormal wear of the teeth, and is most common in _______.
Herbivores
Periodontal disease involves damage to enamel, gums, and periodontal ligaments, and resorption of alveolar bone. What is the mechanism?

Acids and enzymes produced by resident bacterial films
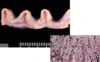
This 48 year old Chimpanzee has lost tooth structure as a result of chewing. What is this called?

Dental attrition
Enamel hypoplasia, seen here in a dog and a calf, can be caused by which diseases in each species?

Dog: Canine Distemper Virus (death of cells that make enamel)
Calf: BVDV infection while in utero
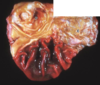
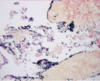
This histology slide taken from a cow shows radiating clubs of eosinophilic material caused by colonies of Actinobacillus lignieresii. What gross lesion would you expect to see in the live cow?

Wooden tongue
A necropsy shows white lesions in the esophagus, and you determine that the causative agent is Candida albicans. What likely caused thrush in this animal?
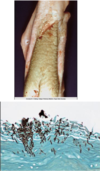
Long term treatment with antibiotics
A 10 year old cat comes in with lesions on the ventral surface of his tongue. You determine that the cat has uremic glossitis. What may be causing these lesions?

Renal disease
MDx: ulcerative and necrotizing glossitis
A FeLV positive cat presents with severe inflammation of the gums. Histology shows lymphoplasmacytic gingivitis, so you diagnose stomatitis. What is the preferred treatment?

Partial or full-mouth extraction of the teeth and debridement of the associated soft and hard tissues.
A cat presents to your clinic for drooling, weight loss, and suspected oral pain. The cat is FIV positive and the owner thinks this illness may be related. You sedate the cat for a full oral exam and discover these lesions in her throat. What is the disease?

Feline chronic gingivo-stomatitis (FCGS)
Chronic ulcerative (lymphoplasmacytic) paradental stomatitis is most common in what age group of dogs?

Older
Vesicular lesions in the oral cavity of small animals can be caused by what immune-mediated diseases?
Bullous pemphigoid
Pemphigus Vulgaris
*Calicivirus can cause oral lesions in cats
A cat infected with calicivirus presents to your clinic with vesicular glossitis. What would you expect to see on histology?
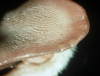
Ballooning degeneration of keratinocytes (intracellular edema)
A farmer calls you out to his farm to inspect some cows that have lesions on their tongues and dental pads. The cows are drooling and some are lame. The farmer said the illness has been spreading rapidly throughout his herd, but no cows have died from it. How is this disease transmitted?

Ingestion or inhalation
*This is Foot and Mouth disease. Viremia follows infection and lesions develop in areas subject to mechanical injury.
Qualified veterinarians perform a necropsy on a young pig who died while under FMD quarantine. This pig didn’t have any vesicles, but “tiger heart” is noted on the report. What was the cause of death?
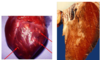
Heart failure due to a malignant form of FMD that causes myocardial necrosis
A farmer decides to euthanize his elderly horse who hasn’t been doing well, and has been off feed for awhile. After euthanasia, you notice these lesions in the oral cavity of the animal. What vesicular diseases are on your differential?
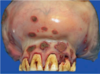
Vesicular Stomatitis ONLY in horses!
You diagnose Vesicular Exanthema in a number of pigs on a farm. What virus are they infected with?

Calicivirus
The erosive, ulcerative stomatitis seen in these cattle can be caused by which viruses?

BVDV
Herpesvirus (Malignant Catarrhal Fever)
A few immunocompromised individuals in a herd of cattle have papules on their nares, muzzle, and oral cavity. A closer look reveals coin-shaped ulcers in their mouths. You suspect that they are infected with a parapoxvirus. What disease are these cows suffering from?
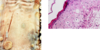
Bovine papular stomatitis
A local farmer calls you out to check on some of his lambs who have stopped grazing and are losing weight. You note pustular dermatitis around the mouth and coronary bands of a 4 month old lamb, and a skin scrape reveals infection with Dermatopilus congolensis. What is likely the primary pathogen involved?

Parapoxvirus
*Orf - contagious viral pustular dermatitis.
ZOONOSIS